From the "Middle reaches" of the industry to the "upstream and downstream"
from "trade distribution" to "processing and manufacturing"
(I) bulk supply chain enterprises: serving the production and circulation of bulk commodities
bulk commodities refer to material commodities that can enter the circulation field, which are different from retail links and have commodity attributes and are used in industrial and agricultural production and consumption in large quantities. According to the attributes of commodity industry, bulk commodities can be roughly divided into industrial products and agricultural products, among which industrial products include iron ore, steel, copper, coal, crude oil, plastic and other black, non-ferrous metals and energy products, while agricultural products include soybean, corn, rubber, wood and other agricultural and sideline commodities.
Bulk commodities have the characteristics of large supply and demand scale, large price fluctuation, easy classification and standardization, strong financial attributes, etc. Commodity supply chain enterprises mainly serve the procurement, inventory and distribution of upstream and midstream manufacturers, including domestic and foreign trade of raw materials and semi-finished products and related supply chain services, so as to ensure the continuity of industrial production process, promote industrial technological progress, industrial upgrading and improve production efficiency.
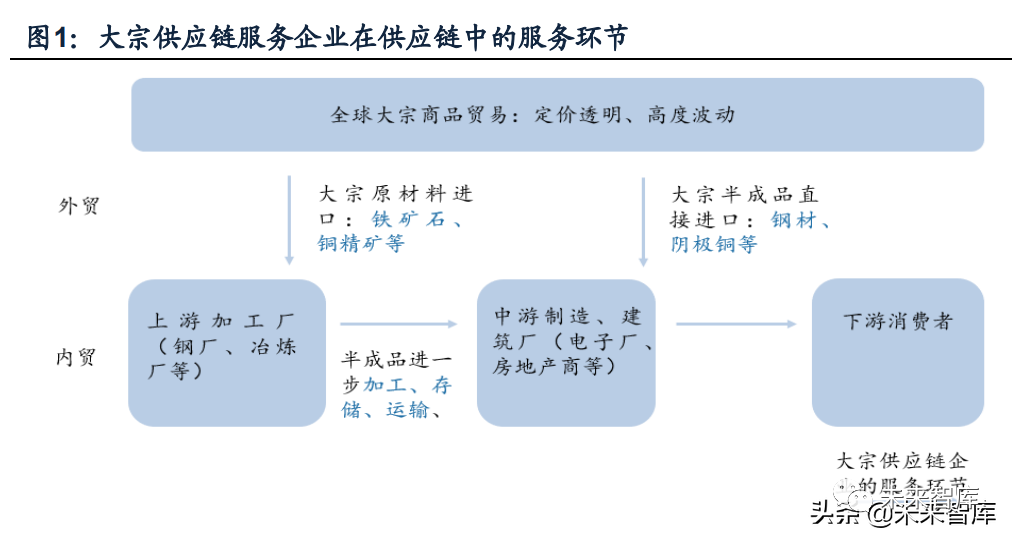
Typical overseas bulk supply chain enterprises include Glencore, Toke, Cargill, Mitsui products, ADM, etc. Their business scope covers metals and minerals, energy products, industrial products and agricultural products worldwide (5.980, 0.18, 3.10%), food mining (or production), processing, refining, transportation, storage, trade and supply chain management services, etc.
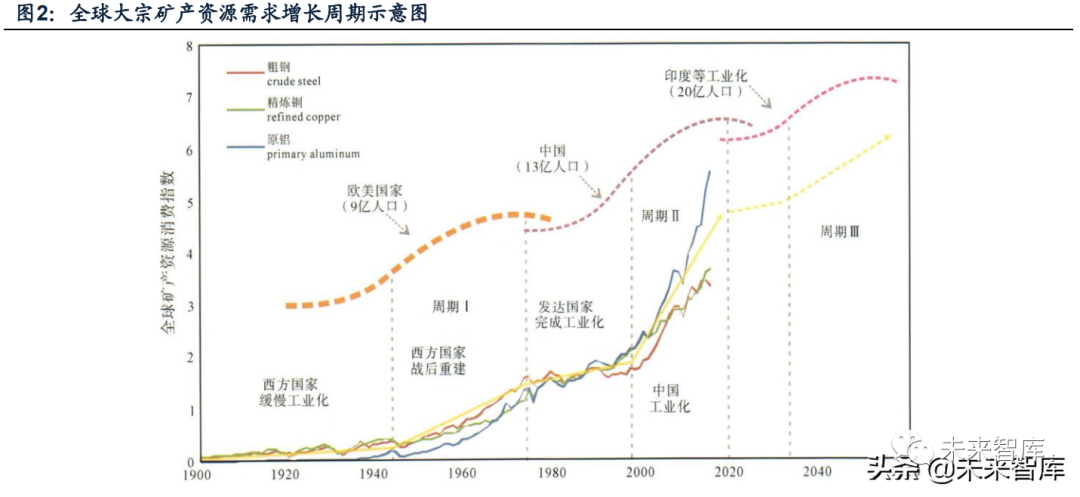
(Ii) demand characteristics: mineral resources consumption "S" trajectory and growth limit
according to the research conclusion of academic paper "the limit and cycle of energy and mineral resources consumption growth", with the development of economy, the per capita consumption of primary energy in developed countries or regions shows slow growth, rapid growth, the S-shaped trajectory of slowing down growth until zero growth or slow negative growth. This evolution law is manifested in the turning point and zero growth point of resource consumption, urbanization rate, economic (industrial) structure, the change points of important indicators of economic and social development such as the degree of infrastructure completion and the level of social wealth accumulation are closely related. That is, with the economic development, that is, the continuous improvement of per capita income or per capita GDP, the urbanization rate, infrastructure construction and social wealth accumulation level continue to increase, the consumption of bulk commodities or resource products will gradually enter the quasi-near saturation state, and the change of consumption structure will cause iron, copper, aluminum and other bulk minerals to reach the per capita consumption limit in the middle of industrialization, and cause the adjustment and upgrading of industrial structure and promote the change of economic structure; Entering the post-industrial development stage, the national economic system with service industry as the main body gradually makes the growth of per capita energy consumption reach the limit value.
Data from overseas countries show that when the per capita GDP exceeds 20,000-22,000 US dollars, the accumulation of social wealth enters a relatively high level, and the consumption of bulk mineral resources is in the stage of zero or negative growth, with low energy consumption characterized by high and new technologies, the tertiary industry with low material consumption has become the main contributor to GDP.
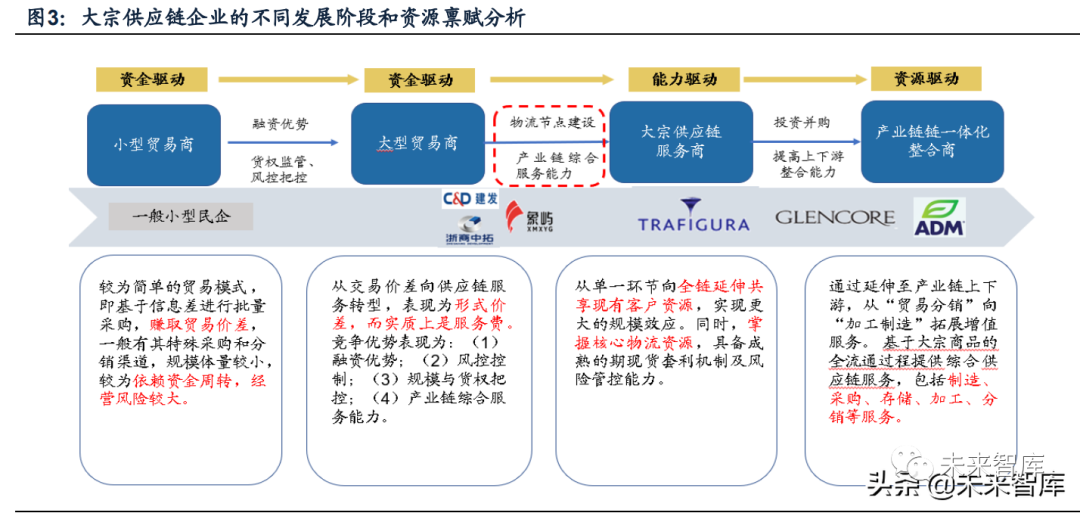
(Iii) business model: based on trade distribution, extending to processing and manufacturing
most of the leading enterprises in overseas bulk supply chain originate from trade, and the core of business model is the transaction price difference, including time price difference and distribution price difference. The defect of the trade pattern is that when the prices of bulk commodities continue to fall and the market becomes more transparent, it often means that the interest spread of traders tends to narrow, and at the same time, it also needs to bear the risk of inventory price decline.
Summarizing the development rules of overseas typical bulk commodity supply chain enterprises, the commonness lies in:(1) trade is still an important part of the business of most bulk supply chain enterprises, but there are few traders who simply buy and sell, at the same time, it is accompanied by comprehensive supply chain services such as procurement and distribution, inventory management, manufacturing and processing;(2) based on the depth of intervention in the industrial chain and the demand for value-added services, it is very important to carry out relevant asset layout, so as to realize the control of the right of goods and strictly control the credit risk;(3) on the development path, based on the middle-stream trade link, to the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain (upstream acquisition of mineral resources/manufacturing and processing, downstream deep processing/distribution) for extension.
Specifically:
1. Toke: comprehensive service provider of commodity supply chain, trade + supporting supply chain services. The main development paths include:(1) strict hedging and financing strategies are adopted in the business process, so that the price fluctuation of bulk commodities is transferred to a relatively smaller basis risk;(2) key logistics nodes of card position, at the same time, strengthen the control over the supply of goods;(3) strategically invest upstream and downstream resources, lock in the purchase agreement of products from upstream high-quality manufacturers, stabilize the upstream supply, and improve the service capability of scale and industry integration.
2. Glencore and ADM: commodity industry chain integrators mainly realize diversified category management through global investment and mergers and acquisitions. At the same time, through the establishment of strong business binding by upstream and downstream enterprises, value-added services such as marketing, logistics and finance are carried out, and processing services are close to the extension of manufacturing industry.
By contrast, through continuous mergers and acquisitions, Glencore's dual identity of "producer + dealer" opens up the industrial chain, which can even affect the pricing of bulk commodities, its asset layout is reflected in the investment in the assets of the whole industrial chain (especially the upstream); While ADM extends from the middle-stream trade of the agricultural product industry chain to the downstream finishing business, value-added services such as destination marketing, loading and unloading, plantation supply chain services and structured supply chain finance.
Toke: value-added services with appropriate weight
(I) Company Overview: focus on trade and supporting services
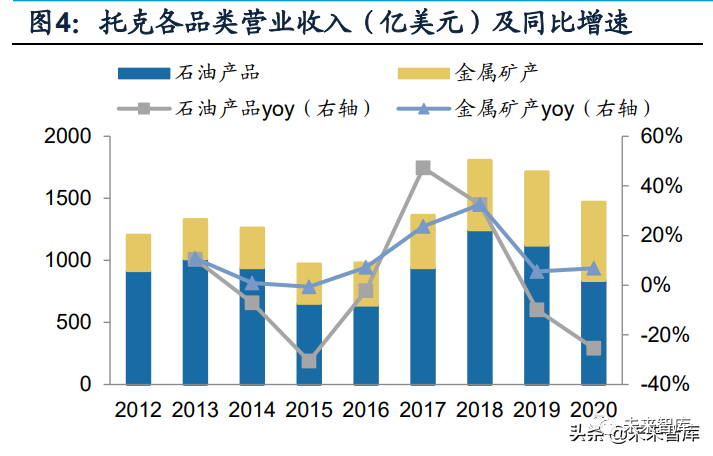
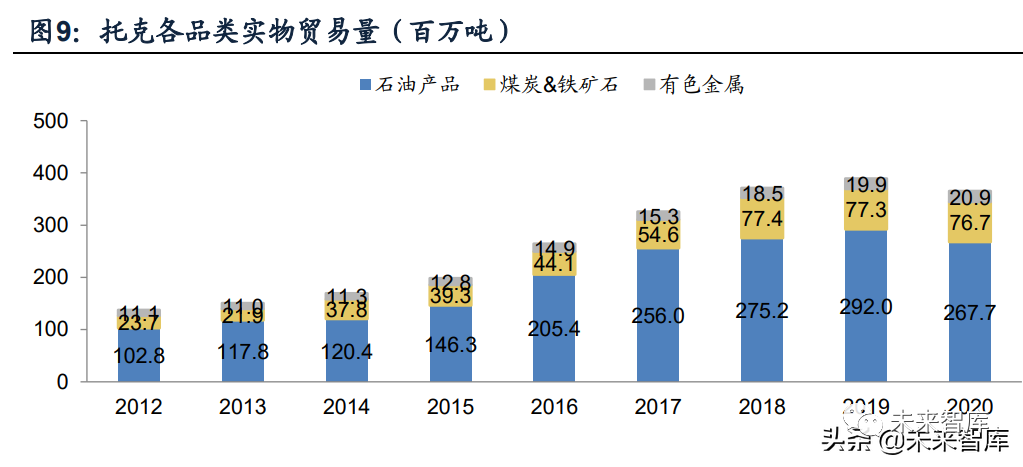
Trafigura Beheer B.V.) founded in 1993 and headquartered in geneva, switzerland, it is currently one of the largest independent commodity traders in the world, with more than 8,000 employees and 80 offices in 48 countries around the world. The company focuses on spot trading services and logistics services for petroleum and petroleum products as well as metals and minerals, and has established global trade business through four departments: petroleum, metals, electricity, renewable energy and shipping. In 2020, the operating income and asset scale of Toke company reached 147 billion yuan and 57 billion yuan respectively.
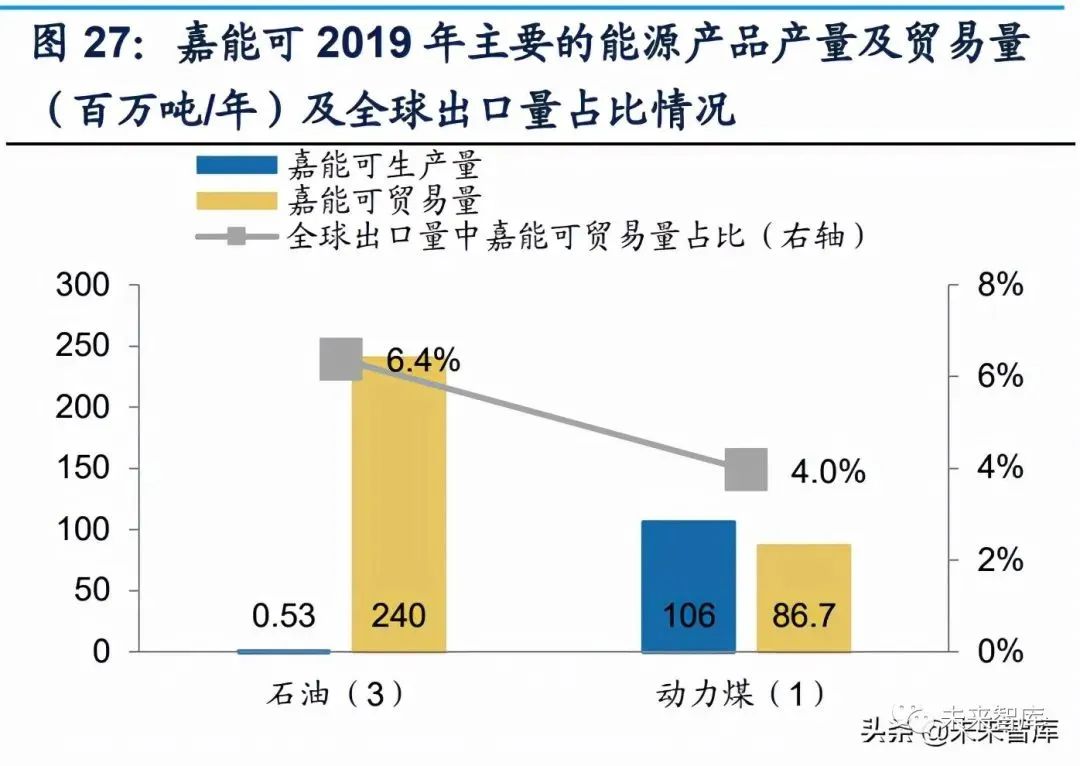
The company's main trade categories include crude oil and petroleum products, non-ferrous metal minerals, coal and iron ore. In 2020, the trade volume of the four main varieties reached 267.7/20.9/56.9/19.8 million tons respectively, the rapid growth of trade volume in the past ten years has made toke rank second in the world in the trade volume of petroleum products and non-ferrous metals.
Toke carries out the procurement, storage, mixing and transportation services of petroleum and petroleum products, metals and minerals worldwide, and carries out arbitrage based on the conversion of geography, time and form in this process. Toke makes use of its advantages of economies of scale to purchase a large amount and reduces the purchasing cost. At the same time, standard derivatives such as futures and exchange are used to hedge parity risks, reduce risk exposure, and avoid regional risks through global procurement. Then, through its mid-stream assets distributed around the world, goods are stored, mixed and transported, and the market is always concerned about looking for real arbitrage opportunities.
(Ii) development process: oil trade started and extended to metal and mineral trade
1. Start-up period (1993-2001): Starting from Latin American oil trade business, it extends to metal mineral trade. Toke company was founded by Marc Rich + Co in 1993. Claude, the executive director of Glencore (predecessor), was founded Dauphin with five other colleagues. At the beginning of its establishment, the company specialized in petroleum metal trade in South America, Europe and Eastern Europe, and achieved profits in the first year.
During this period, the company began to expand in category, region and other aspects through the acquisition of small assets and the formation of strategic alliances. In 1993, the company completed the first asset acquisition-Cormin, a warehouse operator in Peru, and built the South American metal mineral trade business based on this. In the wave of integration of oil giants at the turn of the century, the company strategically acquired the south american oil infrastructure investment and distributor Puma Energy to enter downstream business and strengthen the company's channel capability in oil trade.
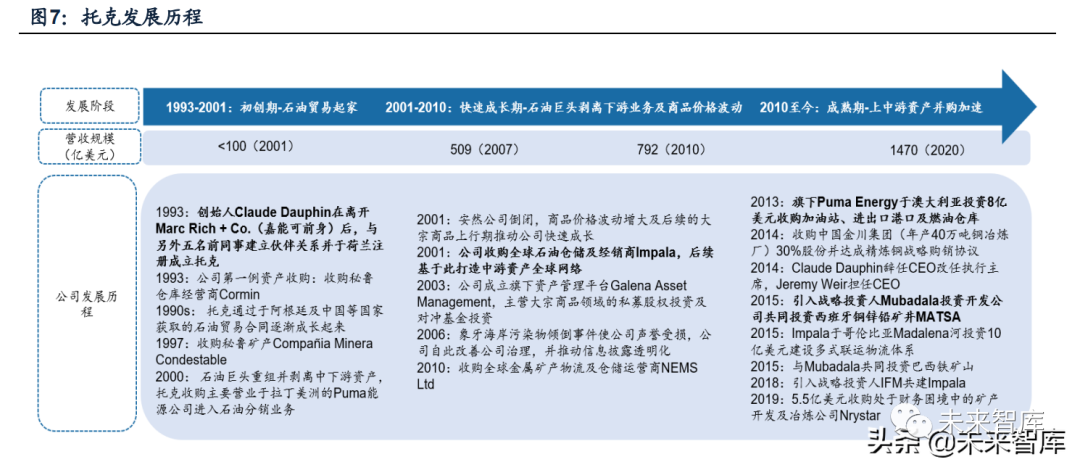
2. Period of rapid development (2001-2010): the contraction of the middle and lower reaches of the oil giant's business and the superposition of the bulk cycle drive the company's rapid growth. The oil giants operating in the integrated industry chain are still trading some crude oil and refined oil products in 1990s. With the extension of the upstream and downstream of the national oil companies and the excess refining capacity since 2000, oil giants gradually integrate and withdraw from the middle and lower reaches of trade distribution business, providing development space for independent commodity traders.
At the same time, factors such as the rapid growth of commodity demand in china and other countries have further consolidated the important position of toke under the background of unbalanced supply and demand of commodities, during this period, the revenue of tok increased rapidly from less than us $10 billion in 2001 to us $79.2 billion in 2010.
3. Mature period (from 2010 to now): the acquisition of assets in the whole industry chain has accelerated. During this period, especially from 2013 to 2015, when commodity prices declined, Toke invested extensively in mines around the world (such as MATSA, Ipe, a Spanish copper mine), and set up Trafigura Mining Group to conduct centralized operation and management of upstream assets; at the same time, build Impala logistics storage platform to integrate the company's global logistics assets (for example, integrate NEMS assets and build a multimodal transport logistics system in South America and other places). Continuous asset investment helps the company consolidate its trade position and enhance its arbitrage ability.
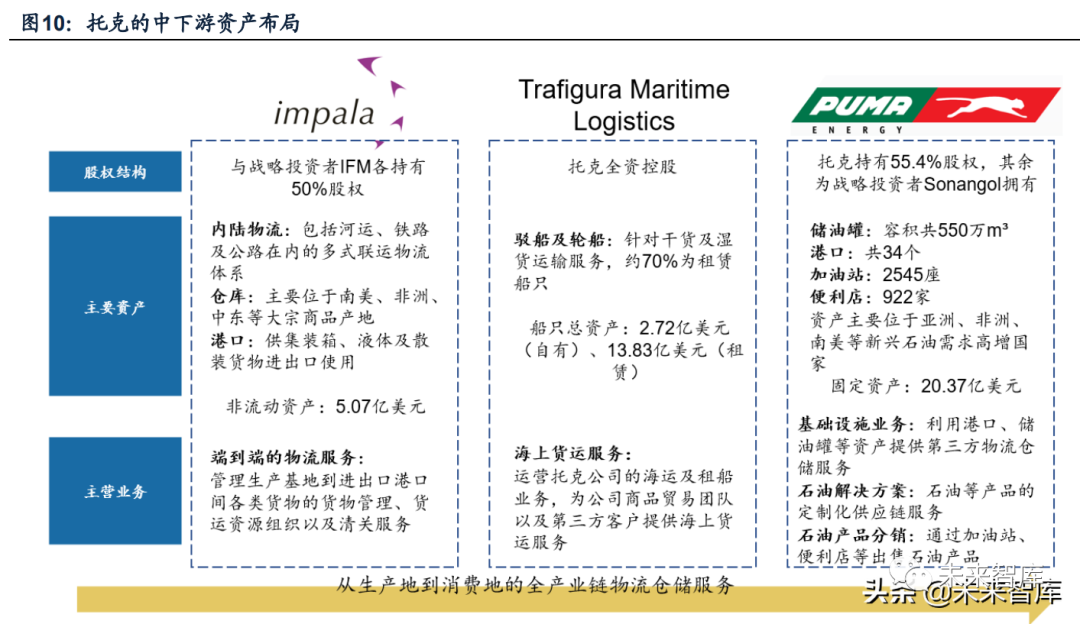
(Iii) asset layout: focus on medium-stream logistics storage assets
toke focuses on trade business, but does not form a two-pillar business model similar to Glencore's "production + trade" through asset mergers and acquisitions. This is mainly because tok insists on the private form of employee ownership to coordinate the conflicts of interest between shareholders and management, while mineral production requires a large amount of heavy asset investment and a relatively high proportion of long-term liabilities and equity financing. Based on this financial structure, the upstream heavy asset layout of Tok is relatively less, and the long-term asset investment is more concentrated on the mid-stream logistics storage assets.
The upstream assets of tok are different from the control of glencore's upstream and downstream industrial chains. Its merger and acquisition idea is to empower the company's commodity trade business, and at the same time share the investment income of the industrial chain to a certain extent. The specific performance is as follows:(1) in terms of investment methods, the proportion of joint ventures is relatively high;(2) taking shares to lock in the purchase agreement of products from upstream high-quality manufacturers, stabilize upstream supply and reduce trade costs.
The asset layout of Toke focuses more on the logistics and warehousing assets in the middle and lower reaches. At the beginning of its establishment, the company began to invest a lot in commodity warehouses, ports and global transportation networks, mainly because the control of goods rights is especially important in the process of commodity arbitrage, and the key logistics nodes of card positions reduce transaction costs.
Specifically, the mid-and downstream Logistics warehousing and distribution assets of toke are mainly operated by Impala Terminals, Trafigura Maritime Logistics and Puma Energy, focusing on the transportation from the production end to the export port, shipping and distribution from the consumer side respectively, form the asset layout of the whole logistics process. In terms of asset categories, Impala and Puma both invest in more ports and storage facilities, which is conducive to maintaining business stability when major fluctuations or structural changes occur in international trade; While trucks, ships, multimodal transport logistics systems such as railways bring higher business volume to toke through cost reduction and efficiency improvement and end-to-end customized supply chain services.
At the same time, Puma Energy is also an important resource extending from tok to the downstream distribution link of the oil industry chain. Since 2000s, it has become a subsidiary of tok, and it has continuously acquired exxon mobil, chevron, etc. located in south america, gas stations, warehouses and other assets in africa and asia have expanded their own business areas and sub-categories (such as aircraft oil, asphalt, etc.), and have now become the key oil distribution channel for toke.
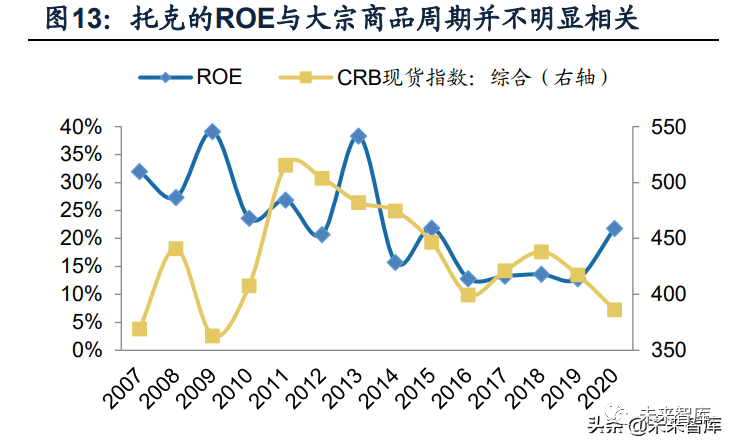
(Iv) financial performance: ROE driven by high leverage ratio and high asset turnover rate
with the increasing distribution of heavy assets, the proportion of fixed assets and joint venture investment in total assets increased rapidly from 2.9 percent in 2007 to 14.0% percent in 2020. Accordingly, tok used the method of duration matching to finance fixed assets, and the proportion of equity and long-term liabilities to total assets increased from 21% in 2007 to 31% in 202020.
In several rounds of commodity cycles since 2007, toke has achieved positive returns at the level of GAAP net profit, with the average ROE reaching 22.85%. The relatively stable profitability benefits from the fact that trafigura specializes in commodity trade business, while adopting strict hedging strategy in the business process, the price risk in the operation is effectively alleviated (transferred to a relatively smaller basis risk).
From the perspective of splitting ROE, it can be seen that the net interest rate of toke is relatively low (the average value is about 0.9%), and the higher ROE level is mainly driven by leverage ratio (about 8 times), on the one hand, the ultra-high leverage ratio comes from the fact that the identity of the private company in tok is less constrained by the capital market. At the same time, most current liability of the traders' balance sheets have corresponding high-liquidity assets (such as cash, inventory, accounts receivable, etc.), so even if the leverage level is high, the liquidity risk is relatively small (the adjusted debt-equity ratio in toke 2020 is only 0.35, assuming that most short-term assets can be quickly realized and repaid by current liability).
Under the highly leveraged financial structure, toke also adopted the asset securitization of accounts receivable and inventory as off balance sheet financing means, which made the company's working capital realize quickly. Specifically, Toke established asset securitization platforms such as TSF and Argo, which can immediately sell accounts receivable to the platform after delivering the goods and obtain cash to repay transactional loans; at the same time, the asset securitization platform raises funds by issuing notes (in which TSF platform is the investment level) and distributes the recovered cash as interest to investors.
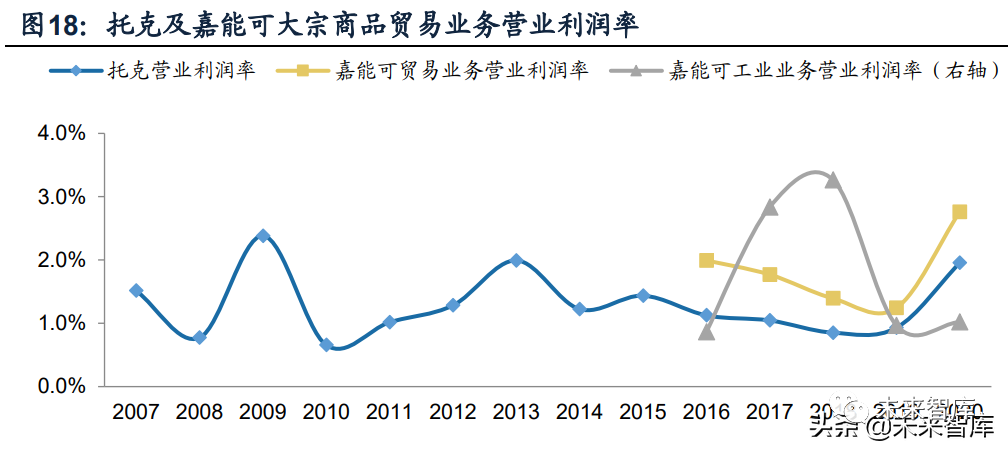
Although price risks were alleviated through hedging and purchase and sale agreements, the financial performance of Toke was not completely irrelevant to the commodity market environment. The net interest rate of Toke achieved a high level in 2009, 2013-2015 and 2020. The high profit of toke mainly comes from:(1) the commodity price fluctuates greatly (the imbalance between supply and demand is relatively high);(2) the current structure of the commodity market is in the state of rising water (contango).
By horizontal comparison, the operating profit margin of toke in the past five years is lower than that of glencore's trade business, with an average of /1.83% respectively, the layout of industrial chain integration or the reason why Glencore's trade business has stronger profitability. In the past five years, the gross profit margin of oil and metal mineral business in tok was /2.41% respectively. In the same period, the EBITDA profit margin of glencore oil and metal mineral trade business was 1.4%/3.2% respectively. For glencore, the mode of more mineral output in the field of metal minerals and sales for trade departments can reduce transaction costs and improve profit margins to a certain extent. But at the same time, the extension of upstream assets will also increase the profit fluctuation. (Report Source: Future think tank)
glencore: continuous upstream mergers and acquisitions
create a "industry + trade" giant
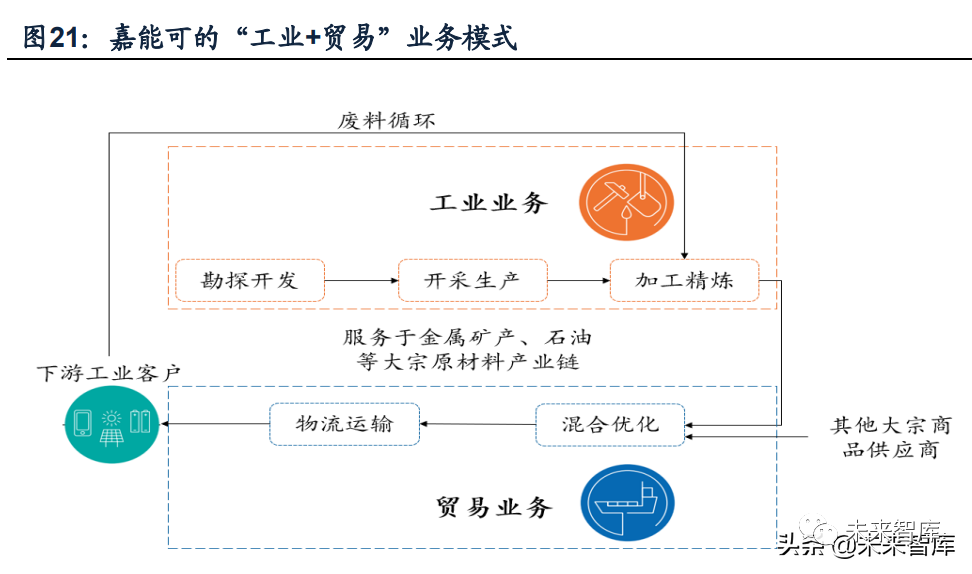
(I) Company Overview: large supply chain giants of "industry + Trade"
Glencore International holding company (AG Glencore International) was founded by founder Marc Rich in 1974 and headquartered in barr, switzerland. It is a world-leading diversified natural resource production and trading company. The company currently specializes in the Industrial (Industrial) and trading (Marketing) business of metal minerals and energy, and its main categories are petroleum, coal, copper, cobalt, zinc, etc, in 2020, the business scope covered more than 35 countries and regions, with operating income and asset scale reaching US $142.3 billion and US $118 billion respectively.
(Ii) development process: oil trade starts and extends upstream mineral resources
at the beginning of its establishment, glencore specializes in global trade services for petroleum and metal products. As the company continues to grow and acquire upstream and downstream assets and equity of metal minerals and energy resources, now it has been built as a giant of the whole industry chain in the world's bulk commodities field, and the large price fluctuation of mineral production business has also increased the volatility of its profits.
1. Start-up period (1974-1994): The company started from oil trade, realizing diversification of categories and extending upstream mineral resources. After 1970s, with the oil-producing countries recovering oil resources exploitation and pricing power through nationalization and the establishment of OPEC, the original vertically integrated industrial chain was broken, and the oil trade between upstream and downstream gradually flourished.
The predecessor of Glencore Marc Rich + Co.AG and vido (currently the world's largest oil trader) were both established during this period and gradually grew up by obtaining oil trade contracts in Iran, the former Soviet Union and other places. Since 1981, Glencore has expanded its trade categories to agricultural products and coal through acquisitions. In 1988, Glencore began to extend its upstream mineral resources. By acquiring 67 percent of the shares of Peru zinc mine, Glencore acquired a controlling stake in the real industry assets for the first time.
2. Rapid development period (1994-2013): continuous acquisition of mineral resources during the upward period of commodity prices, and the transformation to a comprehensive resource company Xstrata the merger. After management buyout and the company changed its name to Glencore, the Company accelerated the process of equity and asset merger and acquisition, during this period, the main targets of mergers and acquisitions were super-large mineral assets and companies (such as copper-cobalt ore Katanga, Mopani, lead-zinc mine Kazzinc and international leading mineral miners Xstrata).
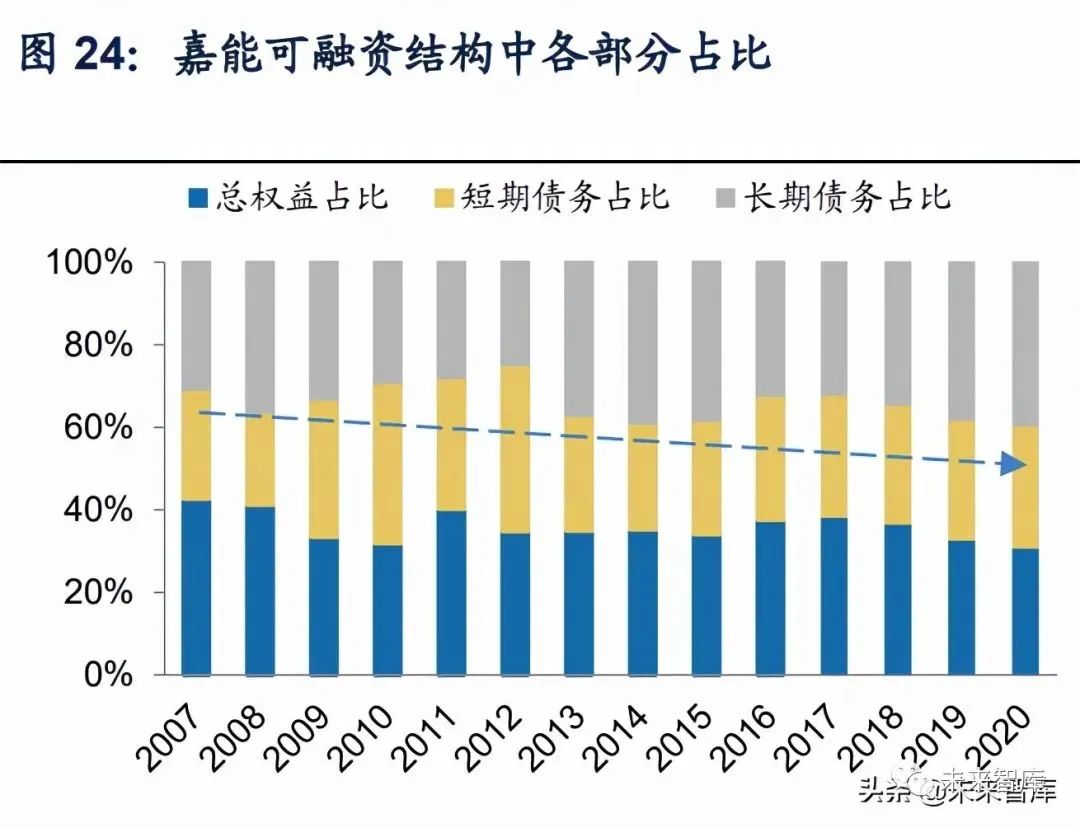
With the acceleration of upstream and downstream mergers and acquisitions in the large upstream period, the sum of the fixed assets and long-term equity investment in glencore's assets increased continuously, and remained above 50% after the completion of the merger with Xstrata in 2013, it has become a relatively small heavy asset company among major international commodities traders. In order to match the rising level of fixed assets, glencore increasingly adopts long-term financing methods such as long-term liabilities. In 2020, the medium and long-term liabilities of the company's financing structure accounted for 39.61%, up nearly 10% from 2007. In addition, the company abandoned the form of private ownership that has been maintained for more than 30 years in 2011 and listed on london and hong kong stock exchange, so as to enter the international capital market to obtain financing channels with wider categories and scope, to support its own expansion process.
3. Mature period (from 2013 to now): Optimization of asset portfolio and equal emphasis on both pillars of production and trade. During the downward period of commodity prices from 2013 to 2015, the Company's mineral production business benefits deteriorated, resulting in the company's net losses of /4.96 billion US dollars in 2013 and 2015 respectively, since 2015, the company began to reduce debts and optimize asset portfolio. For example, in 2016, the company successively sold shares in the agricultural products department and gradually withdrew from the agricultural products business. Since 2017, the company began to expand again and further increased its investment in the assets of the whole industry chain (such as increasing its holdings of copper-cobalt ore Mutanda and Katanga, acquiring Volcan shares of zinc-lead-silver producer and Hail Creek, an australian coal mine, etc.). The continuous integration of mineral resources has made Glencore play an important role in the field of global mineral production. Currently, Glencore ranks first in the world in the production and trade volume of many metal and energy varieties.
(Iii) asset layout: the layout of the whole industry chain, focusing on upstream resource exploitation and smelting processing
glencore actively extends upstream and downstream heavy assets, forming a relatively distinctive asset layout of the whole industrial chain of bulk commodities. Currently, glencore is in industrial metals, iron ore and petroleum fields have subsidiaries or associated companies participating in all links of the industrial chain.
From the category of layout, glencore's capital expenditure is more concentrated in the field of metal minerals. From 2007 to 2020, the capital expenditure of metal and mineral industry accounted for 65%, far higher than that of energy products (27%) and agricultural products (8%). On the one hand, the upstream resources of energy products can be merged with fewer targets. According to Oil & Gas Journal, as of 2020, the proportion of OPEC Oil reserves in global reserves is 71%, and the nationalization of upstream resources makes mergers and acquisitions in the energy field relatively difficult; On the other hand, metal mineral resources are generally concentrated in underdeveloped countries such as south america and africa. Due to changing factors such as trade system, financial resources and political stability, the transaction costs of traders are often pushed up, the vertically integrated m & a strategy can move this part of the transaction into the enterprise to alleviate the transaction cost problem, so glencore is also more inclined to increase m & a in the field of metal minerals.
Judging from the layout of the upper, middle and lower reaches, the asset merger and acquisition of glencore concentrates on resources such as mines and smelters that are mined and processed upstream. From 2016 to 2020, the capital expenditure of glencore's trade business (mainly the middle and lower reaches of resources such as ports and warehouses) did not account for more than 15%, reflecting the sustainable extension of glencore's upstream heavy assets, participating in production, development strategy of value-added processes such as processing.
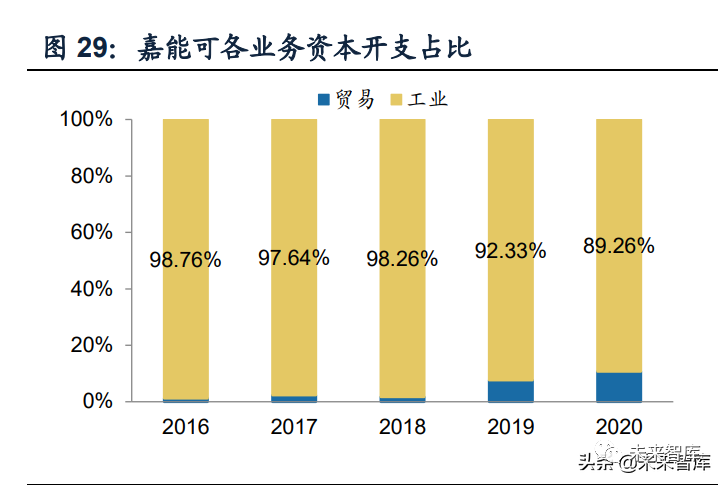
Specifically, glencore has a targeted layout for the control rights and location of assets. Glencore's control over the main upstream mine assets is mainly wholly-owned holdings, while a few are managed in the form of equity participation or joint venture, in order to firmly grasp the mineral control rights, in order to make production reduction or expansion decisions according to the global commodity market situation. Mines in upstream assets are often located in africa and south america, where acquisition costs are relatively low and resources are abundant, while smelting and processing plants are mainly located in europe and america, which are closer to the place of consumption and are industrially developed.
In terms of logistics storage and distribution assets in the middle and lower reaches, glencore is also the core node of card position. For example, several major coal producing areas in australia (such as newcastle) share in coal ports and lay out oil storage and logistics resources in oil trading hub areas, it is conducive to the control of goods rights and effective arbitrage in the company's trade business.
(Iv) financial performance: high fluctuation of net profit caused by mineral mining and processing business
further study the influence of the strategy of continuous asset acquisition of the whole industry chain on the company's financial performance. The results show that:
1. The fluctuation of glencore's net profit is mainly dominated by the change of industrial business operating profit. This part of profit is highly correlated with commodity price because it involves selling semi-finished products and finished products according to market price.
2. The operating profit of trade business is relatively stable, mainly because this part of profit mainly depends on the amount of trade goods * trade price difference, and the amount of trade goods has changed little due to glencore's maturity; the trade price difference is determined by the unequal supply and demand between trading places. It can be kept in a relatively stable range through hedging, locking of purchase and sale agreements and diversification of categories and regions. According to glencore Investor Presentation, the company's trade business EBIT is expected to remain in the range of $22-3.2 billion for a long time.
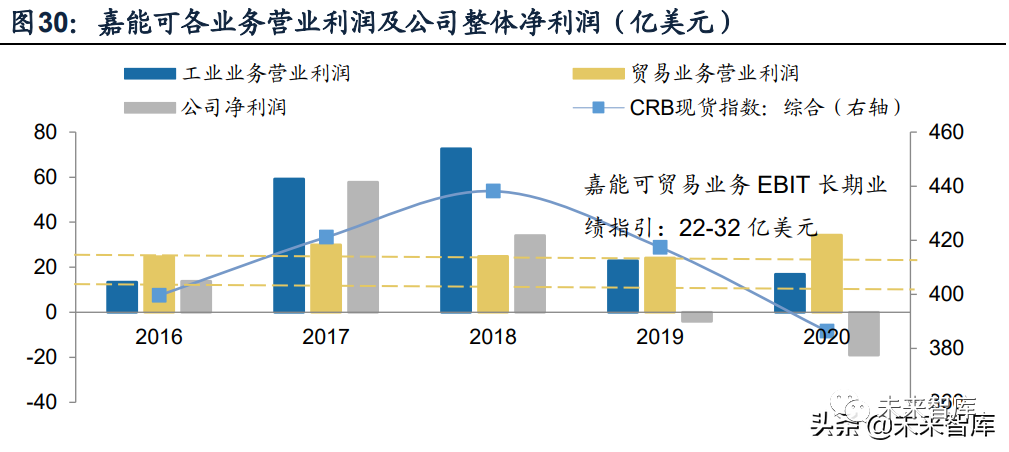
At the ROE level, during 2008-2012, the average value of glencore ROE was 9.52%. After completing the merger with Xstrata, the company completely transformed into a comprehensive resource merchant for bulk commodities, the industrial business increased, while the overall commodity price declined, the ROE fluctuation increased, and the average ROE decreased to-0.88% from 2013 to 2020. The ROE fluctuation after the transformation of glencore mainly comes from the large fluctuation of net interest rate, and the asset turnover rate decreases with the increase of assets; The leverage ratio is generally stable in the range of 3-4%.
ADM: agricultural traders, extending to downstream processing and manufacturing
(I) company overview: the world's leading agricultural products trade and processors
ADM Company (Archer-Daniels-Midland Company) was founded in 1902. at first, it mainly engaged in flaxseed squeezing business. Now it is registered in chicago, usa. It is the world's leading agricultural trade and processors, and also produces human and animal nutrition, with Bunge, Cargill (Cargill) and Louis Dreyfus, they became the four major grain merchants of ABCD ". In 2020, the company's operating income and asset scale reached us $64.4 billion and us $49.7 billion respectively.
ADM's main business can be divided into four sectors, extending from the middle-stream trade of agricultural products industry chain to downstream finishing business. Among them:(1) agricultural services: the acquisition, storage, cleaning, transportation and trade of main agricultural commodities such as oilseeds, corn, wheat, etc.;(2) oilseed processing: process oilseeds such as soybeans into vegetable oil or food products;(3) carbohydrate solution: dry grinding and wet crocking corn and wheat to produce sweetener and starch products;(4) nutrition: sell essence, pigment and other nutritional raw materials and provide relevant solutions.
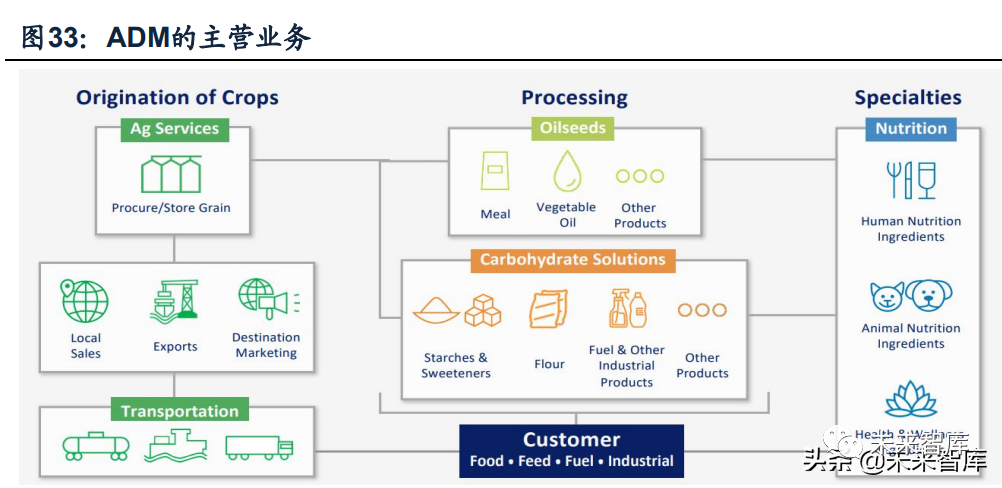
Agricultural bulk commodity trade accounts for a relatively high proportion of the company's revenue structure, reaching 49.0% in 202020. Although ADM has extended its main scope to the rough processing and finishing end of agricultural products downstream of the industrial chain, the company's agricultural service business is still one of its most important businesses, it includes not only traditional trade and transportation, but also some value-added services such as destination marketing, loading and unloading, plantation supply chain services and structured supply chain finance. In 2020, the operating income of ADM agricultural services reached us $31.71 billion, accounting for 49% of the company's total revenue.
(Ii) development process: mid-stream traders started and extended to downstream finishing business
1. Early stage of development (1902-1945): at the beginning of the company's establishment, the company mainly engaged in oil seed processing, with a continuous expansion of scale and a continuous expansion of business categories. The predecessor of ADM company was founded by two founders John W. Daniels and George A. Archer Linseed Daniels. Thanks to good operation and continuous profit reinvestment, the company continued to expand and acquired several oilseed processing enterprises in the midwest of the united states in succession, renamed ADM in 1923. The company also actively expanded its business categories, successively entering the corn processing, soybean squeezing and flour production business. By the end of world war ii, the company had been able to produce hundreds of agricultural semi-finished products, and to paint, leather, printing, paper and other industries provide industrial oil products and related services.
2. Rapid growth period (1945-1990s): the company has become a diversified agricultural products trade and processing group operating globally. After world war ii, with the rapid recovery of american economy, the company's agricultural products processing business developed rapidly. During this period, the company's business has undergone three major changes:(1) rough machining extends to fine machining: ADM deepens the physical processing degree of products and reduces the proportion of raw materials/semi-finished products sold, according to the management's estimation, 40% of the sales growth during 1939-1949 came from higher-order processing methods and extending to the downstream of the industrial chain;(2) continuing to expand overseas: the company began to expand to europe and south america in 1960s, cooperate with local interest groups to invest in the establishment of processing plants and ports, etc. (3) the investment in midstream assets has increased and the establishment of a global trade and transportation network: the company has successively entered the river barge business and truck transportation business, and invest in the great lakes region and overseas ports.
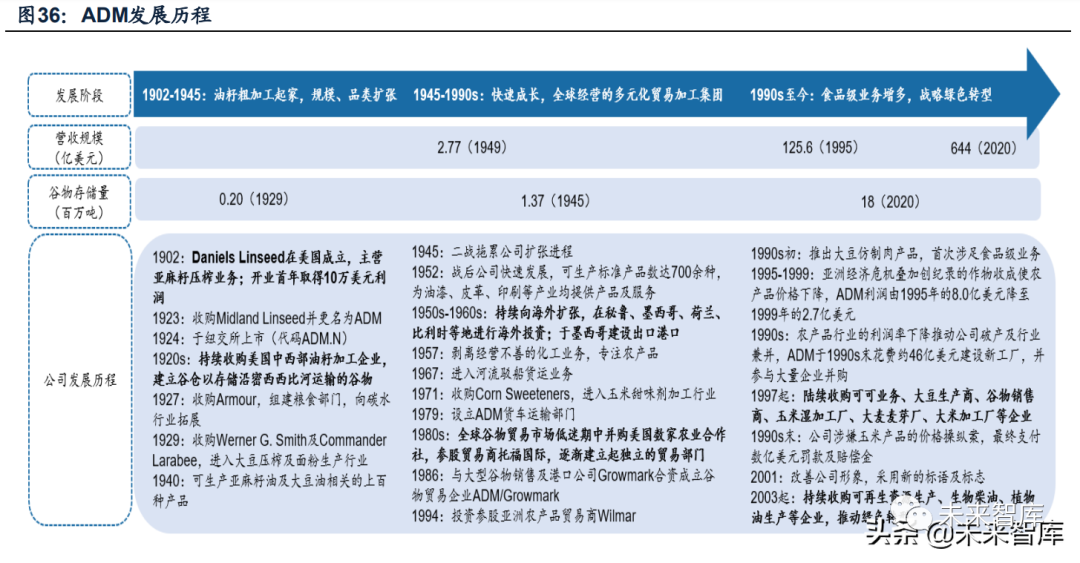
3. Mature period (1990s-present): plus-sized industrial integration during the downward period of price to promote the development of green health related businesses. In the late 1990 s, the company continued to promote the improvement of corporate image and green transformation, and successively entered the business of spices, agricultural owner information services, pet food, probiotic production, etc, in 2016, the nutrition department was taken as the main business department to conduct financial accounting alone, and continued to expand to downstream agricultural products with more complex chemical structures.
(Iii) asset layout: middle-stream layout global logistics network, downstream layout "processing + distribution" business
ADM's asset layout is more concentrated in the middle and lower reaches, rather than extending upstream planting. The main reason is that traders often lock in crop supply by cooperating with farms. ADM will provide upstream farms with a series of supply chain services including fertilizer, information consultation, supply chain finance, etc. to improve the viscosity of upstream suppliers and achieve strong binding to upstream channels, equity participation and related asset layout are not required.
Compared with other industrial commodities, agricultural trade has a higher demand for investment in midstream assets. This is mainly because:
(1) the production and consumption of agricultural products are highly mismatched in time and space. In terms of time, crops tend to mature in a specific season, while consumption is relatively uniform in a year; In terms of space, high yield production of crops often has regional requirements, while consumption areas are relatively scattered. The large amount of revenue at maturity makes the storage capacity required higher. (2) agricultural products are more prone to loss and have higher storage requirements: compared with industrial products such as steel and petroleum, agricultural products often have requirements on the storage environment in terms of humidity and temperature, good storage requires higher investment in midstream assets.
ADM has more asset layout in the middle reaches, forming a global asset layout network. In terms of mid-stream assets, the company mainly invests in procurement facilities, warehouses and ports, among which procurement facilities and warehouses are mainly located near crop production sites, firmly grasping the right of bulk agricultural products.
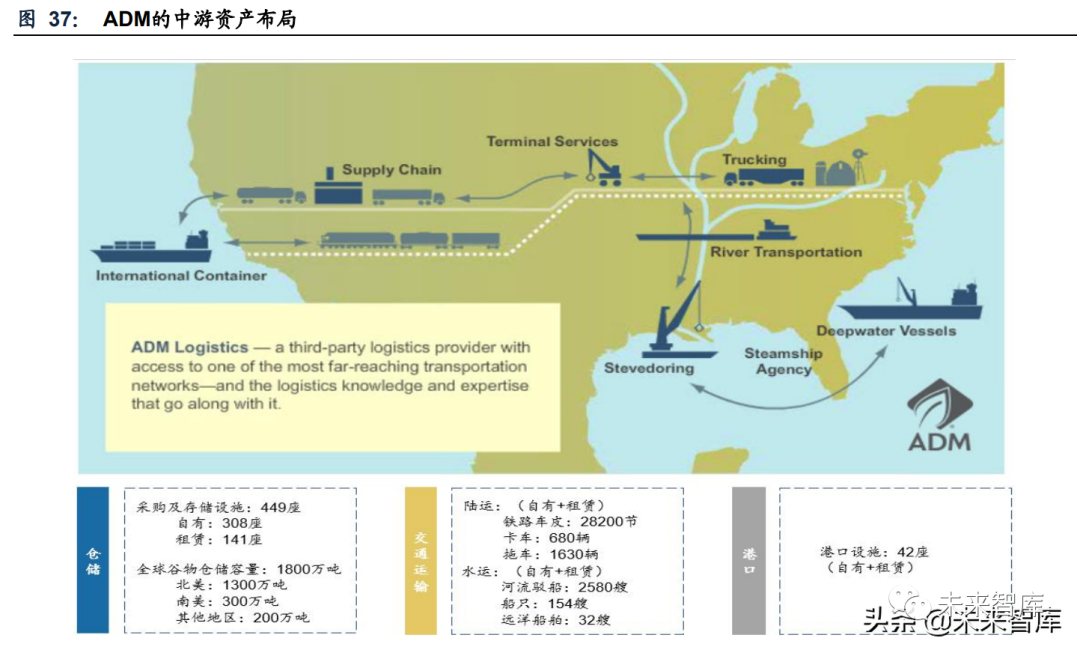
In terms of means of transportation, ADM Logistics, a subsidiary of ADM, specializes in global Logistics of agricultural products, and has built a multi-modal Logistics system of railway, highway and waterway, at present, the subsidiary delivers billions of dollars of bulk food-grade products every year. In terms of water transportation, the company invests in river transportation and ocean going vessel, and provides loading and unloading services connecting river transportation and sea transportation and steamboat agency services. At the end of 2020, ADM had nearly 2,000 ships; In terms of land transportation, ADM has an end-to-end transportation network in the united states, including trucks, railway vehicle cover and trailers. It also provides supply chain management, optimization, integration and consulting services for upstream and downstream enterprises.
On the downstream asset side, ADM started from crude oil seed processing and gradually extended to downstream finishing. By the end of 2020, ADM had 296 factories, 23 processing plants, flour mills, milling plants and other assets, of which about one third were located overseas, and the production was aimed at downstream food and beverage producers, all kinds of agricultural processing products such as industrial customers and nutrition customers. The integration of the middle and lower reaches of agricultural products trade processors is mainly due to the high similarity between the required logistics storage resources and supply chain management capabilities: the trade of agricultural products raw materials and semi-finished products is aimed at large quantity, wide geographical distribution, downstream groups with different businesses have common requirements such as corrosion prevention and cleaning in storage and transportation.
The vertical integration between the middle and lower reaches is conducive to the enhancement of ADM's industrial chain position and the improvement of profit margin. Raw material trade products are relatively standardized. The average operating profit rate of non-trade business of ADM from 2004 to 2020 is 6.5%, while the average operating profit rate of trade business in the same period is only 2.4%.
(Iv) financial performance: in recent years, ROE has stabilized at around 11%
the proportion of fixed assets of ADM has been stable in the range of 20%-25% since 2011, (the continuous decline from 1999 to 2008 or related to the increase in the proportion of trade business with light assets, the revenue of trade business was 4.6 billion in 2001 and 34 billion us dollars in 2009, the proportion increased from 25% to nearly 50%), between the main layout of the middle-stream assets and glencore, which owns more upstream minerals.
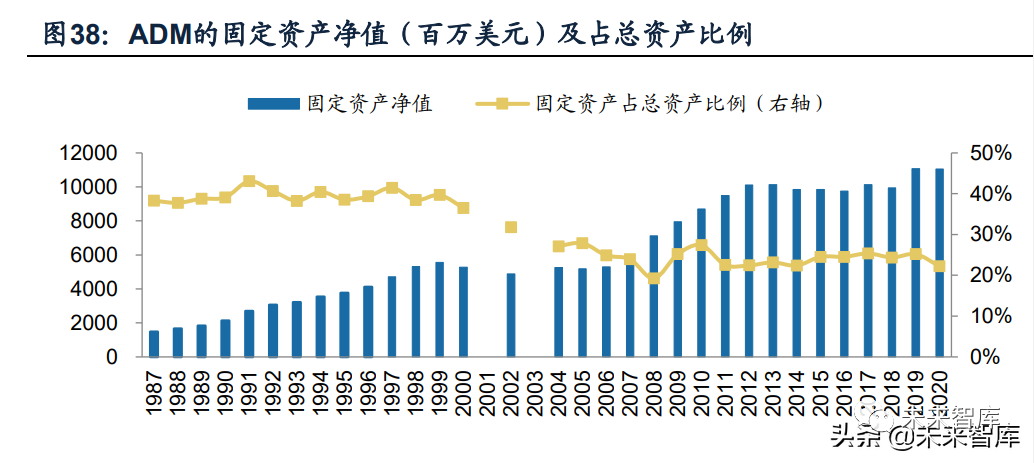
ADM's profitability is relatively stable, with an average ROE of 11% from 2004 to 2020, which is relatively stable in several rounds of agricultural product bulk cycles. The correlation between ADM's financial performance and price is not strong, which may be related to the business layout of mid-stream trade and downstream processing in the agricultural product industry chain. Agricultural service business (agricultural products trade business) is closely connected with downstream processing business. A certain proportion of agricultural products raw materials of ADM are sold to its own downstream processing department, therefore, the trade process with relatively large price fluctuation is transformed into internal transactions of the company, which to some extent reduces the overall profit margin of the company affected by price fluctuation. At the same time, the company's trade and processing businesses adopt hedging methods, and their respective operating profit margins are fluctuation within a narrow range in the range of 1%-5%/4%-9% in several rounds of agricultural production bulk cycles.
Evolution of overseas leading business models
extend to the whole industry chain and broaden the value-added services of processing and manufacturing
(1) typical two types of models: commodity supply chain service providers vs industrial chain operators
first of all, from the perspective of the development path of the three companies, there is a process of continuous expansion of business categories and regions. Both glencore and tok have gone through the process of infiltration from focusing on oil trade to the fields of coal, metal minerals and agricultural products; ADM is the production and trade of agricultural products processing and semi-processed products from the initial agricultural products oilseed corn wheat and other trade.
In addition, summarizing the development rules of overseas typical commodity supply chain enterprises, the commonness lies in: ( 1) trade is still an important part of the business of most bulk supply chain enterprises, but there are few traders who simply buy and sell;(2) based on the depth of intervention in the industrial chain and the demand for value-added services, it is very important to carry out relevant asset layout, so as to realize the control of goods rights and strictly control credit risks;(3) on the development path, based on the middle-stream trade link, extend to upstream and downstream of the industrial chain (upstream acquisition of mineral resources/manufacturing and processing, downstream deep processing/distribution).
The difference lies in: tok focuses on trade and reduces volatility through hedging means such as hedging; At the same time, it becomes a commodity supply chain service provider through the key logistics nodes of card position and the ability to provide industrial chain integration services. Glencore and ADM are modes of deeper integration of the industrial chain.
Glencore mainly invests upstream mineral resources in order to make production reduction or expansion decisions according to the global commodity market situation, while ADM mainly extends to downstream roughing and finishing ends, provide comprehensive services including traditional trade and transportation, as well as some value-added services such as destination marketing, loading and unloading, plantation supply chain services and structured supply chain finance.
Compared with the driving factors of ROE, we can also see the differences in the profit models of the three companies: among the three companies, toke has the highest ROE and is mainly driven by higher leverage ratio and turnover rate. This is also consistent with the company's trade-oriented and abundant financing and hedging methods. Comparing the ROE driving factors of glencore and ADM, we find that the ROE fluctuation of glencore mainly comes from the large fluctuation of net interest rate, while the net interest rate of ADM is obviously more stable. This difference is largely due to the difference in its operating categories. (Report source: future think tank)
(2) the long-term financing ratio of heavy asset mode is high to match the investment demand of fixed assets
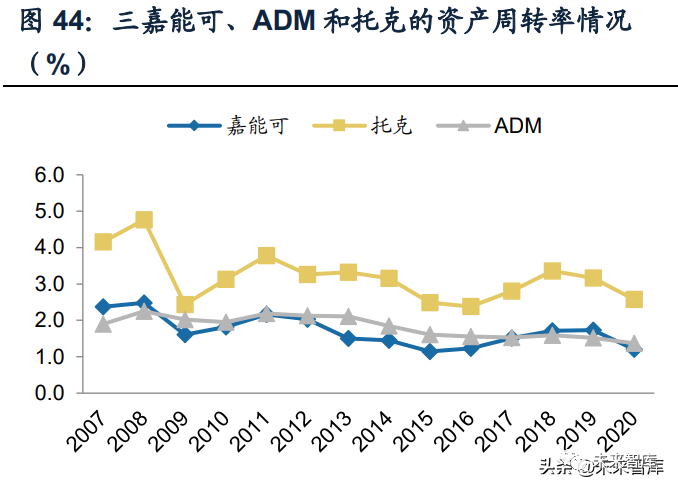
although upstream and downstream mergers and acquisitions are a major feature of the expansion of more overseas bulk trading enterprises, this does not mean that bulk trading enterprises will definitely move towards the development mode of heavy assets. Compared with the development process of overseas bulk trading giants, we find that their expansion process is accompanied by more investment and mergers and acquisitions, such as glencore's merger and acquisition of upstream mineral resources Xstrata, toke's investment in logistics resources such as the middle-stream storage terminal and ADM's investment in downstream food processing plants, etc. However, compared with the fixed assets ratio of major overseas bulk commercial and trade enterprises from 2007 to 2012, it can be found that not all enterprises develop in the direction of paying attention to assets.
The difference of fixed assets ratio of different enterprises is mainly due to the difference of their business categories. Observe the fixed assets investment of each enterprise in different business categories in each link. For different business categories, overseas traders have the following characteristics in investing in upstream, middle and downstream:
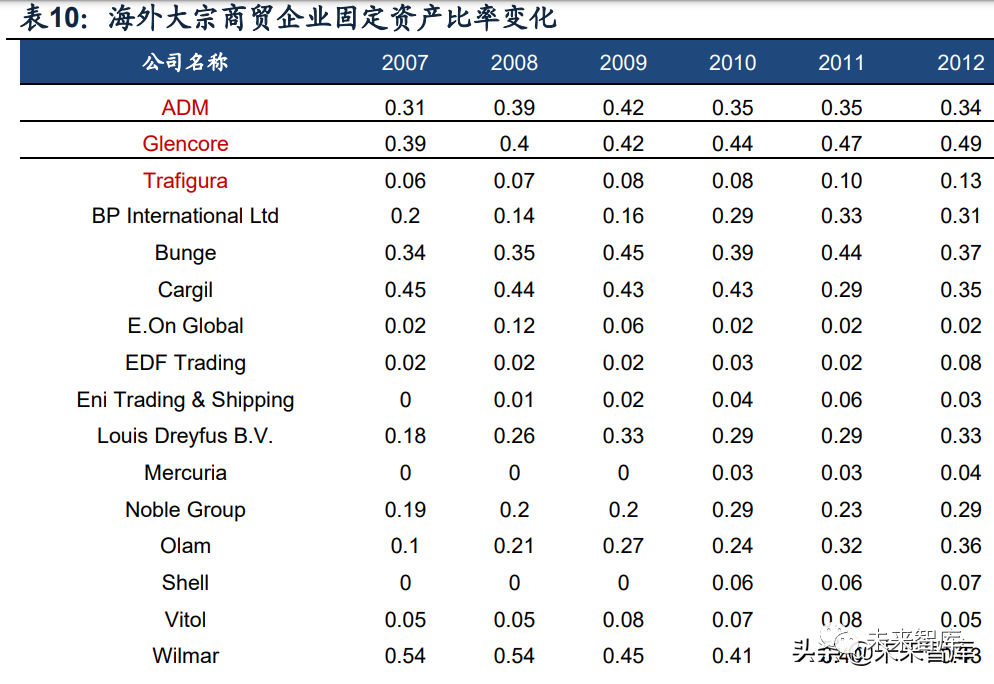
1. Upstream: upstream investment is more in petroleum and mineral fields, and also in some agricultural products business fields. While having a strong correlation between upstream investment and business category, it is also related to the business strategy adopted by the company. The upstream investment is generally to reduce the negotiation risk caused by price fluctuation, but sometimes it can be realized through acquisition agreement. In addition, upgrading upstream production efficiency by providing professional knowledge is also one of the reasons why traders choose to invest and acquire upstream resources.
2. Midstream: overseas bulk traders have the most common investment in midstream assets, and this feature is most obvious in the field of agricultural products management. Due to the fluctuation of supply and demand and regional distribution differences in bulk supply, the arbitrage of time and space for bulk traders is mainly realized through the storage and transportation of intermediate links. The investment of key logistics nodes in the middle reaches can control the core nodes and master the supply of goods. Of course, not all logistics assets need to be invested, such as bulk carriers and oil tankers with high standardization and strong resource substitution.
3. Downstream: investment in downstream assets is mostly in agricultural products and oil fields. It is generally aimed at fast-growing regions in emerging markets or developed countries. Due to the limited number of wholesalers and distributors, downstream service providers have greater influence on the supply chain. Traders can influence terminal prices by investing in various downstream links. The investment in the middle and lower reaches in the petroleum field is relatively common, which also stems from the fact that oil giants focus more on the upstream exploitation and production links and reduce their involvement in the middle and lower reaches. Some agricultural products fields also have this characteristic.
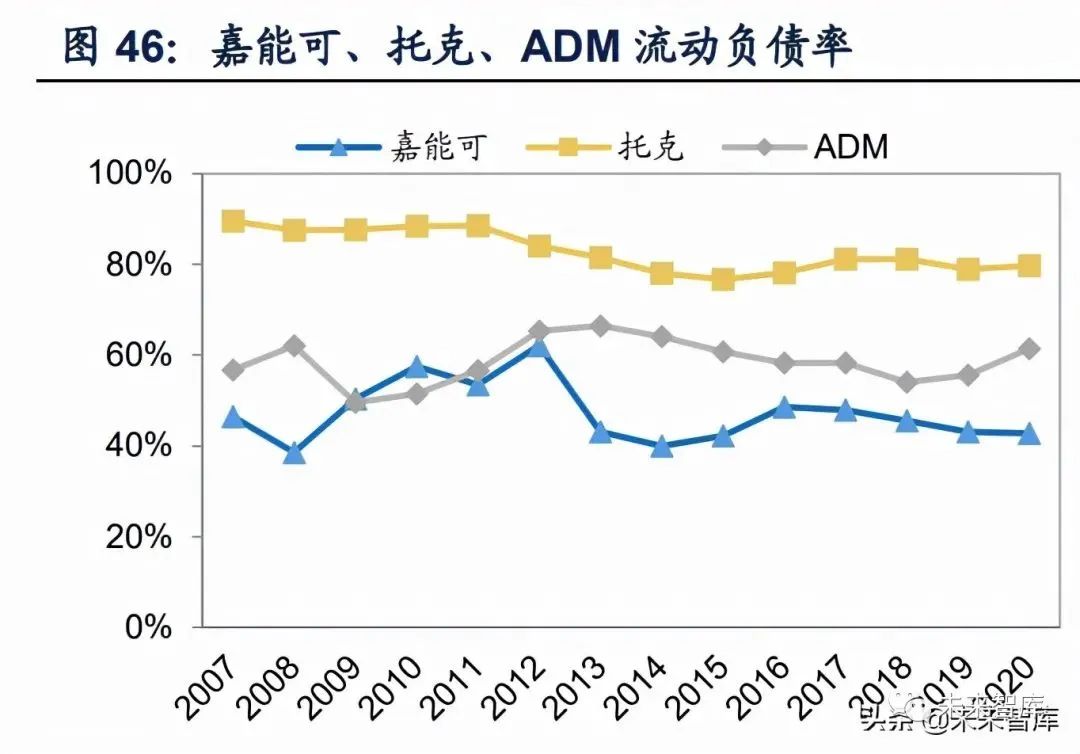
Traders adopting different operation modes also have great differences in debt structure. Toke group, which adopts a light asset operation mode, has few own assets and needs a large amount of financing to meet the capital demand for driving its business expansion. Since 2007, the asset-liability ratio has remained at a high level of more than 84%, the asset-liability ratio of glencore and ADM remained at 50%-70% in the same period.
Glencore and ADM, which are both heavy asset models, also have differences in asset-liability ratio and liability structure due to different business categories and different choices in investing in upstream and downstream industries. Glencore mainly invests in upstream oil wells and mines, with a large demand for funds, and needs more long-term financing to support its business strategy; While ADM chooses to extend to the downstream agricultural products deep processing industry chain, mainly investing in food processing plants, new product research and development center and so on, the relative demand for funds is small. At the same time, due to the cyclical characteristics of agricultural products, short-term financing can also support part of its heavy asset investment, so the current debt ratio is higher than glencore.
Chinese characteristics: technology empowerment, chain extension, value-added services
(1) bulk demand: change the growth rate without pessimism
in the past ten years, china's bulk commodities have been growing at both ends of production and consumption, and the bulk commodity market as a whole has formed a huge volume scale. For 10 important commodities such as crude oil, coal, crude steel, soybean and corn, the CAGR of domestic production and consumption from 2010 to 2019 was 2%/3% respectively.
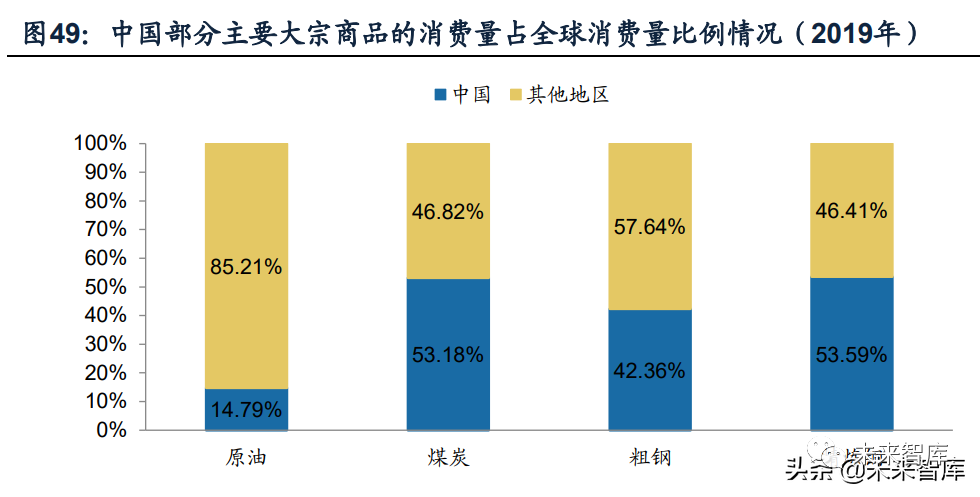
At present, china has become one of the world's major commodity production and consumption countries, among which the consumption of coal, crude steel, refined copper and other commodities ranks first in the world, and the consumption of other important commodities has also ranked first in the world.
From the structural point of view, the growth rate of commodity demand shows a trend of differentiation (colored> agricultural products> black ≈ energy). We select the consumption situation of typical varieties in some bulk commodities to analyze the bulk growth situation of various categories in the past ten years (note: steel and coke represent black categories; Thermal coal and refined oil represent energy class; refined copper and refined nickel represent colored products; Corn represents agricultural products). It can be seen that the growth rate is colored> agricultural products> black ≈ energy. Considering the background of carbon neutrality and the incremental demand of non-ferrous metals driven by industrial transformation and upgrading (according to the data of the international copper association, the copper used for fuel vehicle bicycles is about 23kg, the amount of copper used for pure tram bicycles is about 83kg), and the physical consumption of non-ferrous metals is expected to continue to maintain rapid growth in the future.
(Ii) business model: transformation from traders to integrated supply chain service providers
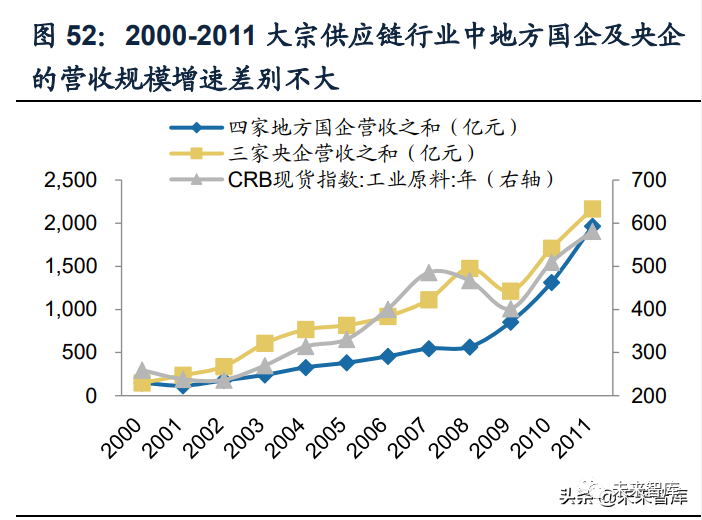
the start of china's industrialization has brought about a strong growth in demand for bulk commodities. Short supply and asymmetric information mean rich trade profits. After 2012, with the macroeconomic downturn and the continuous improvement of market transparency, the profit margin of traders has been significantly narrowed, and even the risk of inventory price decline needs to be borne. During this period, some traders of central enterprises and local state-owned enterprises gradually transformed into the form of advance-type price difference, nested value-added services such as logistics, financing and information, and controlled bulk exposure. Due to the lower operating efficiency and poor transformation effect of the central enterprises with better resource advantages, the revenue was greatly impacted during the decline of commodity prices from 2013 to 2015. In contrast, some local state-owned enterprises with market-oriented genes have achieved relatively steady growth.
At present, compared with typical overseas commodity supply chain service providers, the obvious difference between chinese commodity supply chain enterprises is that due to the incomplete credit system, china's bulk supply chain enterprises undertake the financing function of european and american commercial banks; While the european and american service provider model has stripped off the financing function, and processing and other services are close to the extension of manufacturing industry.
Taking zheshang zhongtuo's bulk commodity engineering material distribution business as an example, this paper further analyzes the business model of china's bulk commodity supply chain comprehensive service. The distribution of engineering materials takes the investment owners of large construction enterprises or basic construction projects as the service objects, distributes materials for their engineering projects, and provides procurement plan management, resource organization, transportation and distribution, advance of receivables, settlement services to price management and other engineering materials supply chain management portfolio services. After comprehensive investigation, the company evaluates the risk of project receivables, participates in bidding, signs a steel supply contract with the customer after winning the bidding material supply package, and stipulates the daily online price (market price) for issuing the plan order. 50 yuan/ton + freight 60 yuan/ton package delivered to the construction site, and the goods will be paid off on the 30th. Judging from the proportion of service fees, the proportion of capital service fees exceeds 50%.
After the transformation, large supply chain enterprises provide downstream manufacturers with financial, logistics, processing and other services, and make profits by charging service fees. Bulk supply chain enterprises can hedge the risk of price fluctuation through hedging, but when the price of bulk commodities falls and downstream customers default on credit, the rapid realization of margin and commodities is particularly critical. This depends on:
(1) lower capital cost;(2) risk control capability (including secondary pricing, formula settlement, margin, disposal of goods rights, and hedging in futures market, etc.);(3) scale and industry comprehensive service capability.
We subdivide the profit sources of the existing supply chain service provider model, mainly including the basis trade income, capital service fee, logistics value-added service fee and procurement integration service fee. In actual business, bulk supply chain enterprises sign package prices based on physical quantity according to specific service contents and risks. If small and medium-sized enterprises own their own procurement and logistics, it is difficult to manage and has no advantage in cost. However, leading supply chain companies combine industry and commodity analysis capabilities, logistics network capabilities, capital credit strength, etc. by integrating demand, provide customers with a package of solutions and benefit from basic services and value sharing.

(Iii) the most feasible growth path of china's bulk supply chain companies
1. Technology empowerment. Logistics finance makes the industry expected to get rid of capital restrictions and change its profit model to diversified comprehensive service capabilities. Due to the different credit environment, we believe that there are some differences between the current business model of china's commodity supply chain service providers and overseas business models: at present, the balance sheet driving characteristics of china's commodity supply chain industry are obvious, capital gains (advances) and service fees contribute mainly gross profit. Relying on the resources of local state-owned enterprises and market-oriented incentive mechanism, leading companies have accelerated their expansion with the advantage of lower capital cost.
In the current incomplete credit environment, bulk supply chain service enterprises need to advance payment for downstream industrial enterprises when carrying out business, and their business model shows obvious capital-driven characteristics, the asset-liability ratio of supply chain enterprises is generally high. By 2020, the average asset-liability ratio of five major supply chain leading enterprises reached 72%, of which zheshang asset-liability ratio was 76%. For the consideration of controlling debt service risks, the asset-liability ratio of supply chain enterprises was close to the "ceiling" level.
The logistics financial model helps the company to get rid of capital restrictions and transform its profit model to diversified comprehensive service capabilities. Under this mode, the company acts as a financing intermediary, and serves the financing credit of downstream enterprises and the risk control of banks based on the real enterprise operation data collected by itself in the supply chain business.
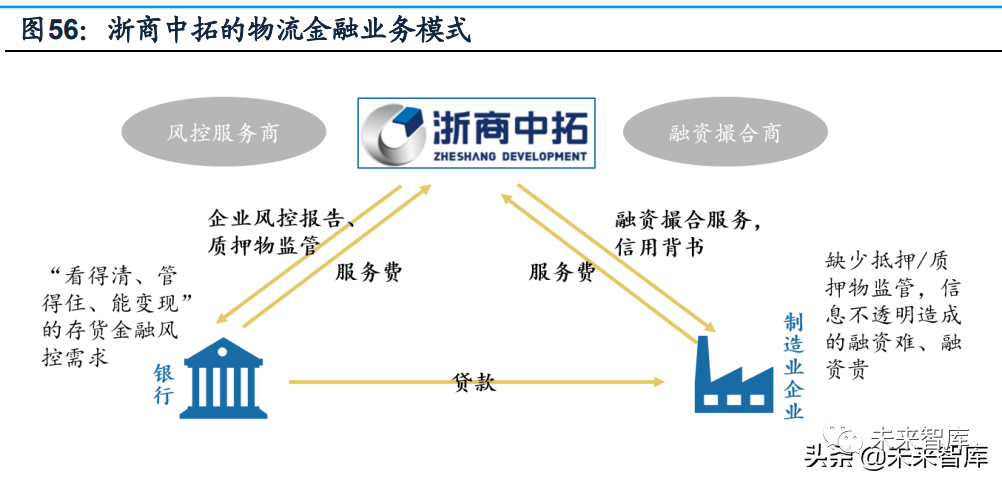
This model is different from the supply chain financial services led by banks before:(1) banks and bulk supply chain companies perform their respective duties (banks act as direct financing intermediaries, supply chain enterprises act as "risk control service providers and financing matchmakers");(2) the business model of bulk supply chain companies no longer depends on capital-driven, but through logistics, information flow (industry consulting), business flow (agency execution) and other methods provide customers with comprehensive diversified services. Profits come from diversified service income, while ROE depends on service net interest rate, leverage ratio and asset turnover rate.
Chain extension and value-added services are shown as the development path of overseas commodity supply chain companies. The reference for chinese commodity supply chain enterprises lies in:(1) firstly, based on financing costs, risk control ability and deep service ability of industrial chain, the growth path of leading companies has the process of continuous expansion of business categories and regions;(2) extending to the whole industrial chain based on the middle trade link, expand value-added services from "trade distribution" to "processing and manufacturing.
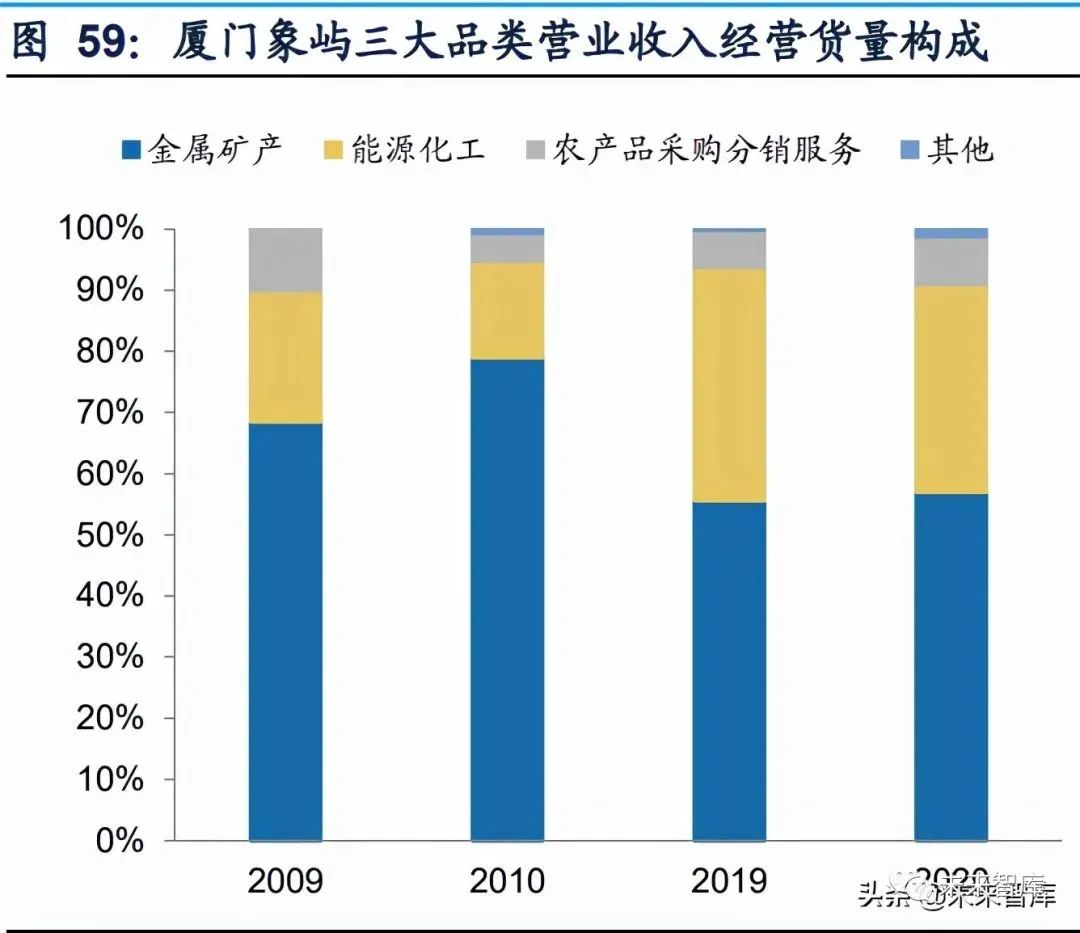
1. Category and regional expansion. For example, in recent years, xiangyu xiamen has continued to promote product mix optimization and build a more comprehensive commodity mix system. Judging from the three major commodity categories of metal minerals, energy chemicals and agricultural products, the company's current income structure is 66%, 22% and 11% respectively, and the proportion of operating volume structure is 58%, 35% and 8% respectively. At the same time, from the perspective of risk control, the company also limits the largest share of a single commodity category, and properly matches and controls the scale of each category when it grows.
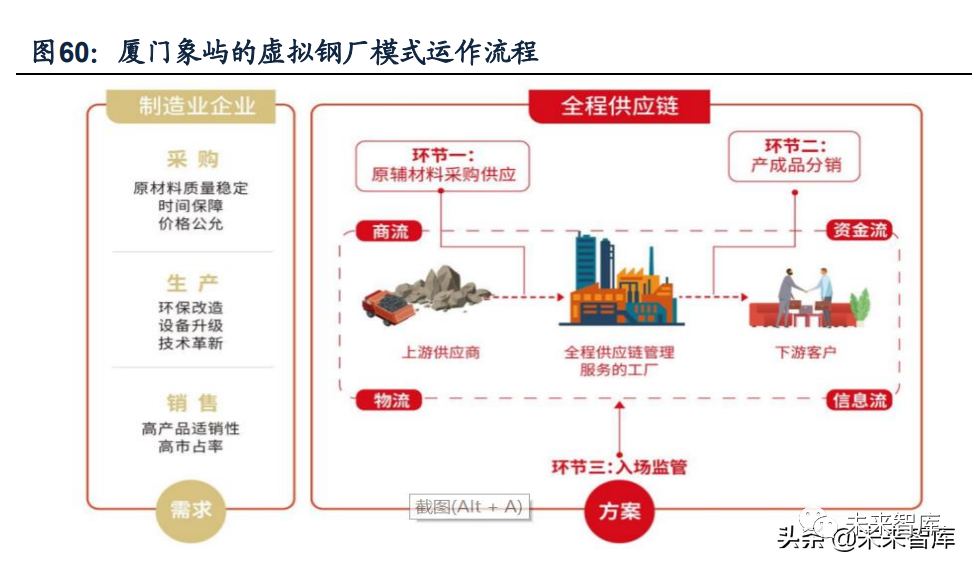
2. Expand value-added services from "trade distribution" to "processing and manufacturing" along the upstream and downstream of the industrial chain. At present, the virtual steel mill model in xiangyu, xiamen is a useful exploration for chinese large supply chain enterprises in the deep integration of industrial chain. The virtual steel mill model is a brand-new model for xiamen xiangyu to develop its metal mineral supply chain business. The difference between the virtual steel mill model and the general metal mineral procurement and distribution business lies in one more link-admission supervision. Under the virtual steel mill mode, the company is responsible for the whole process from raw material procurement, dispatching management team to factory site supervision to finished product distribution, which is the concrete embodiment of the whole supply chain service mode.
The downstream of steel is relatively scattered, but the upstream concentration is relatively high, which leads to the downstream enterprises in a relatively weak position in terms of transaction and bargaining, the upstream distribution channels are not smooth enough, and the overall efficiency of the supply chain is general. By building a supply chain service platform to add value to the whole supply chain, xiangyu is committed to solving the problems of unstable supply of raw materials, opaque prices and unsmooth distribution channels. Through value-added services, both sides can achieve win-win results, and xiangyu shares value-added benefits with steel mills. (Report source: future think tank)
the main links of virtual steel mill mode include three parts: raw and auxiliary materials, finished products and admission supervision. The whole operation process is as follows:
(1) identification of industrial projects: before the implementation of the virtual steel plant project, the factory should be analyzed and identified in depth;
(2) procurement of raw and auxiliary materials: after completing the project evaluation and deciding to enter, xiangyu is solely responsible for the procurement and supply of raw and auxiliary materials in the factory, enjoying the ownership of raw and auxiliary materials and being responsible for distribution and transportation;
(3) admission supervision: complementary advantages, taking advantage of the technical level advantages of virtual steel mills and ready-made production equipment, sites and rich production experience, at the same time, xiangyu stationed a management team for admission supervision, form a comprehensive control of the production process to reduce risks.
(4) sales of finished products: after the production of the virtual factory is completed, the finished products will be pledged to xiangyu, which is responsible for distribution. The company implements a strict risk control system for virtual steel mills. Generally, it selects large products with strong circulation ability, easy realization and large market space to carry out business, and ensures that the products can be sold quickly through its own channels, grasp the right of goods in the transaction process.
The business of "full supply chain management service" contributed about 57.8 billion yuan in revenue in the first half of 2021. the steel works involved include xiwang special steel, Delonghi steel and so on, and successfully applied the model in the steel and aluminum industry chains, the number of projects increased to 7.
Xiangyu agricultural products: actively explore the whole process service of agricultural products. Under the whole-process supply chain mode of agricultural products, the company deeply intervenes in the pre-production, mid-production and post-production of agricultural production, provides production factors to participate in the production link, and takes charge of the operation of the circulation link by using the logistics storage network and distribution system. In the production process, the company carries out cooperative planting with farmers, providing farmers with a series of comprehensive planting services including capital, seed fertilizer, agricultural machinery, technology, insurance, etc., and sharing profits after deducting the interest of capital cost, in addition, the company is also developing its own mode and becoming a powerful supplement to cooperative planting. In the circulation link, the company uses the distribution logistics system to provide raw grain for large-scale breeding, feed and grain deep processing enterprises through the acquisition, drying, storage and transportation links to obtain income.
Zheshang zhongtuo: actively explore new energy business. In 2017, the company established a wholly-owned subsidiary zhongtuo electric power to provide external integration services of new energy supply chains such as photovoltaic, wind power, coal-to-electricity conversion, etc. It is internally responsible for the development of the group's new energy business. As of 3Q21, china tuo electric power has established good cooperative relations with industry leaders such as china power construction, huawei, jingao and longji, continuously expanding products such as electrolytic nickel, nickel sulfate and recycled lead. At the same time, it has set up a new energy storage technology department, explore equity investment in energy storage industry and enrich profit models. In addition, the company is also trying to combine resource recycling with new energy business to explore battery recycling business.
* Disclaimer: the content contained is from public channels such as the Internet and WeChat public accounts. We maintain a neutral attitude towards the views in this article. This article is for reference and communication only. The copyright of the reprinted manuscript belongs to the original author and organization. If there is any infringement, please contact Huanyi world customer service to delete it. Mainly
Mainly

 Polyurethane
Polyurethane

 Fine Chemical
Fine Chemical












.png)



