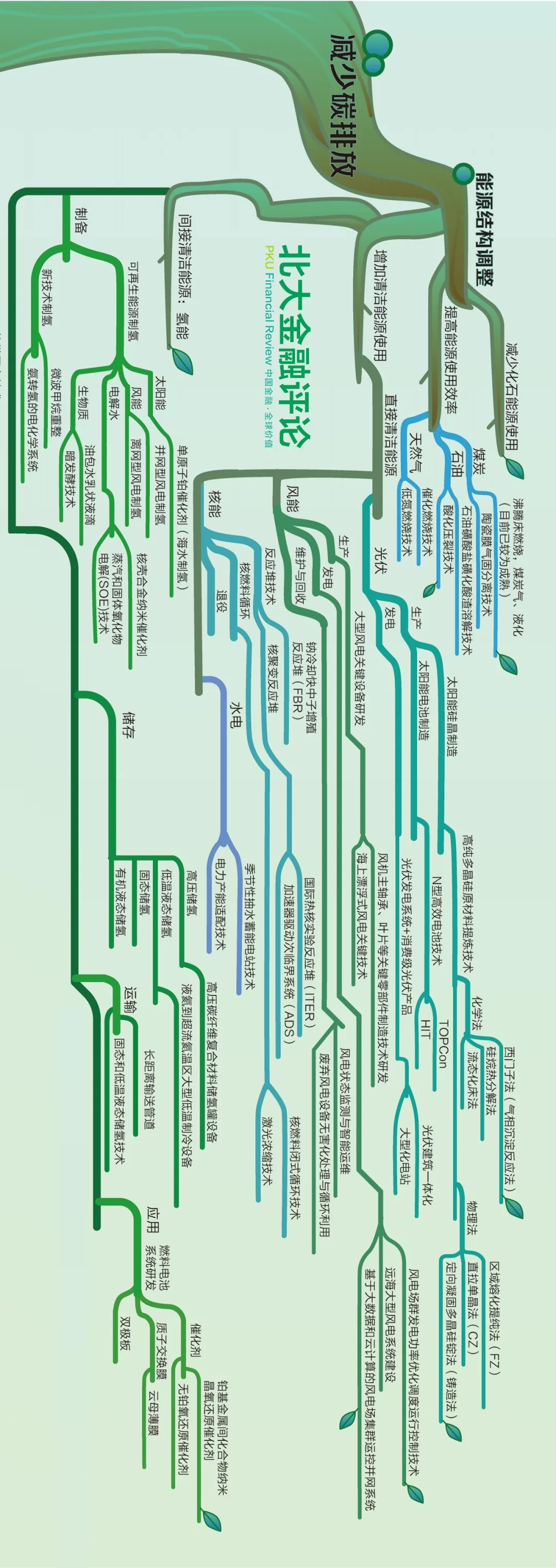
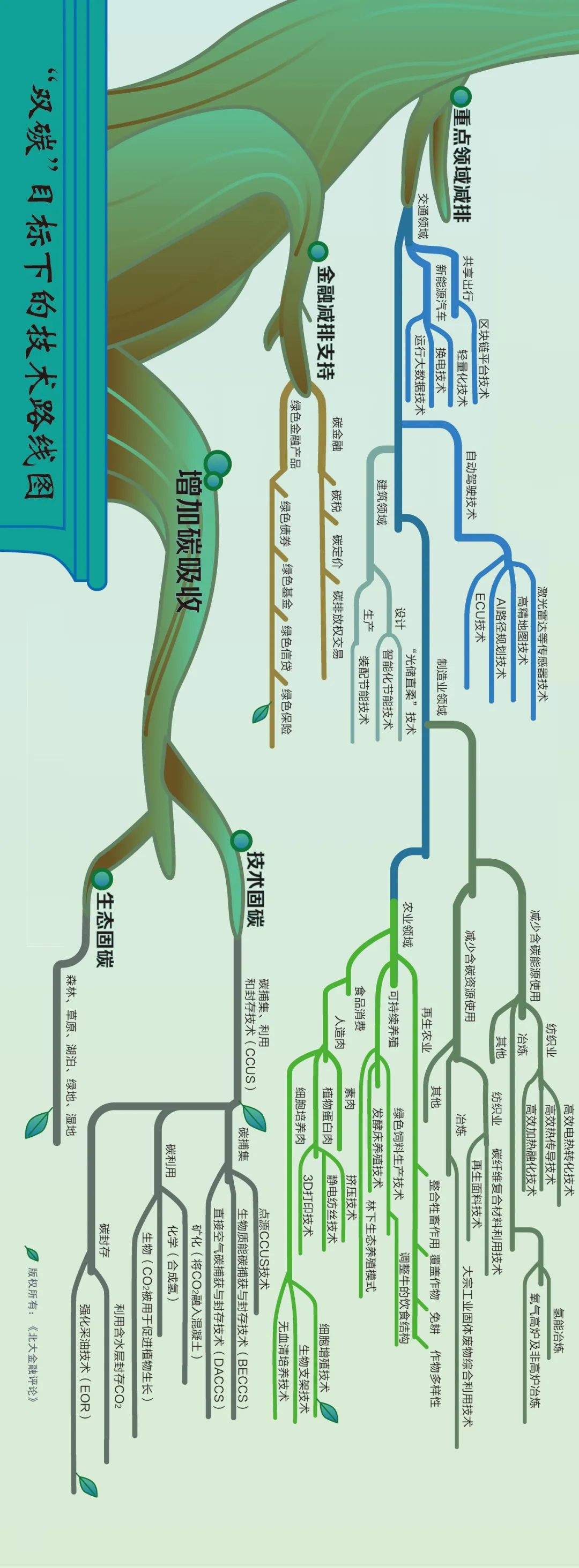
Recently, the "Peking University Financial Review" released a technology roadmap under the "dual carbon" goal, including two main routes to reduce carbon emissions and increase carbon absorption. Among them, reducing carbon emissions includes three routes: energy structure adjustment, emission reduction in key areas and financial emission reduction support, and increasing carbon absorption includes two routes: technological carbon sequestration and ecological carbon sequestration. This is refined step by step to get a complete technical roadmap.
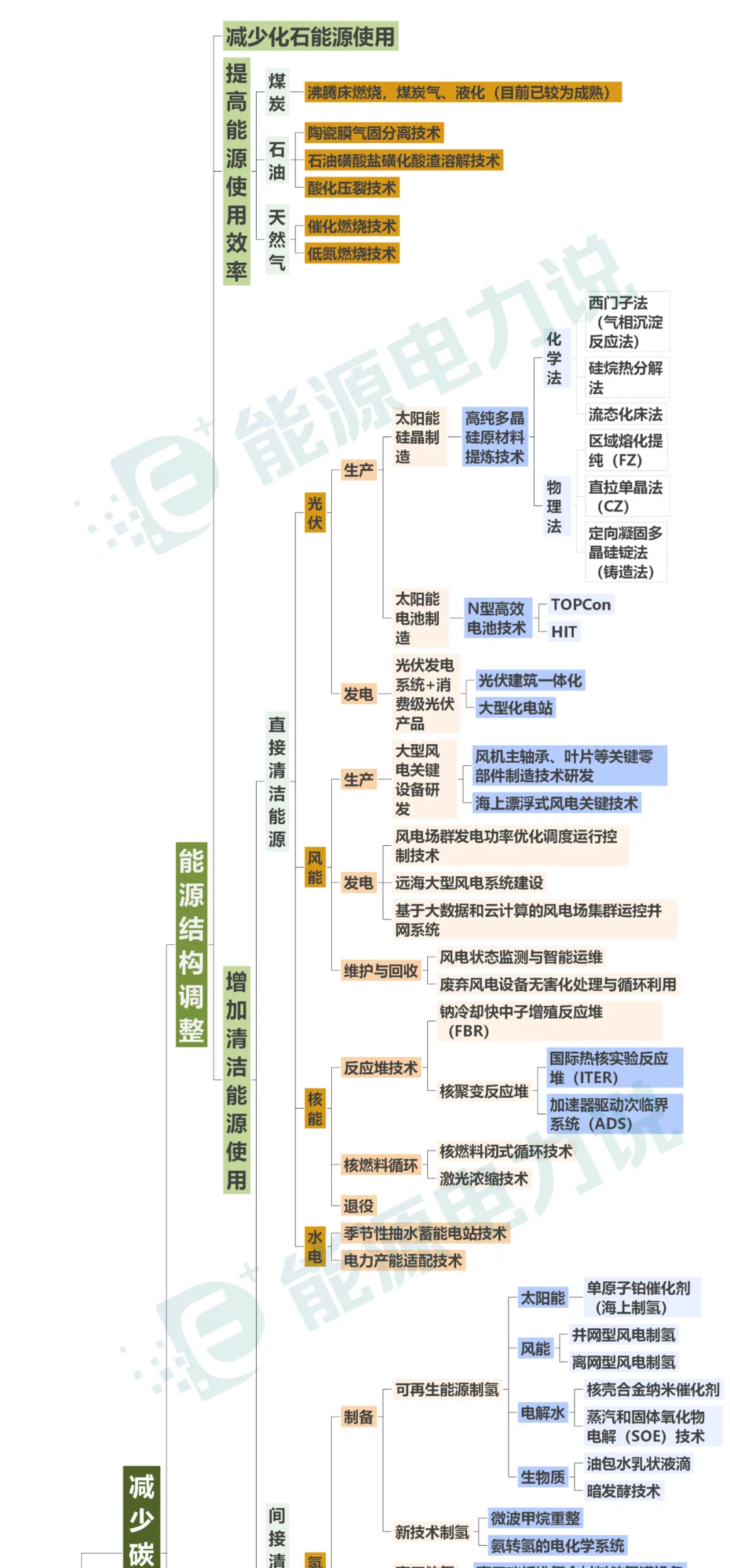
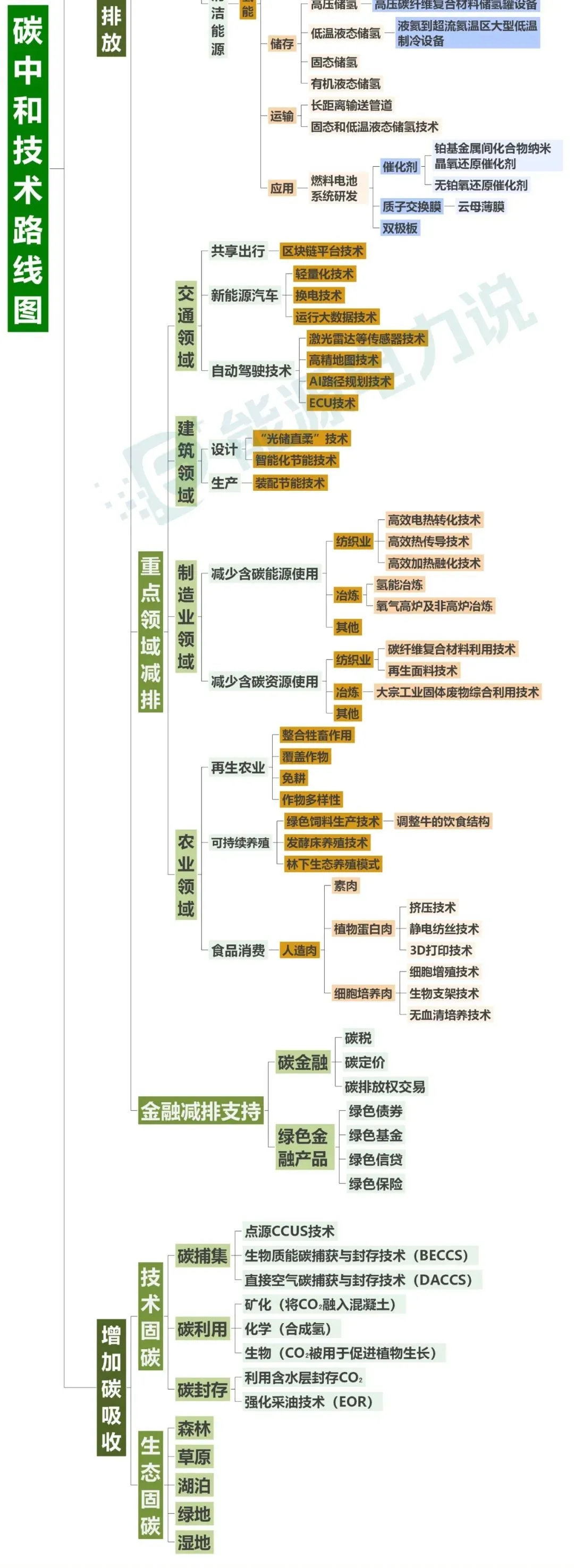
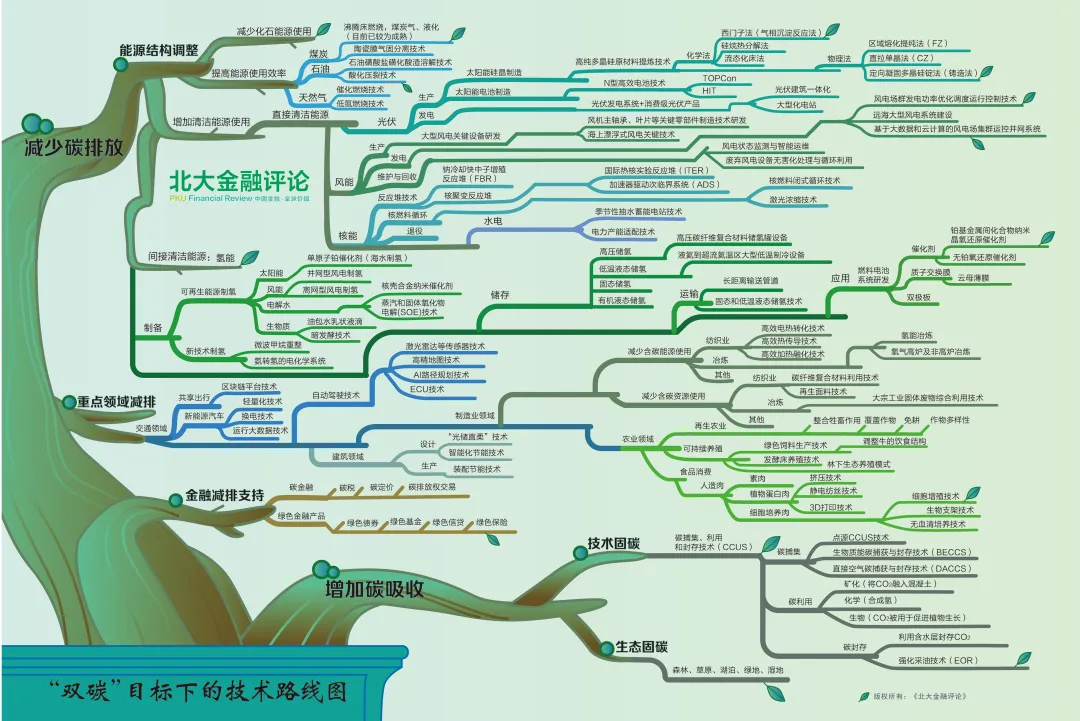 Divide the above picture into two parts for easy reading (please watch it horizontally)
Divide the above picture into two parts for easy reading (please watch it horizontally)
what are the technologies of low carbon, zero carbon and negative carbon?
According to the documents of the Ministry of Education:
key carbon emission reduction technologies (low carbon): Carry out technological innovation around the green development of fossil energy, low-carbon utilization, pollution reduction and carbon reduction, and focus on strengthening the multi-energy complementary coupling, low-carbon building materials, Low-carbon industrial raw materials, low-fluorine raw materials and other source emission reduction key technologies development; strengthen the development of key technologies for emission reduction in processes such as the integration and coupling of the whole industry chain/cross-industry low-carbon technologies, low-carbon industrial process reengineering, and efficiency improvement in key areas; strengthen the coordination of pollution reduction and carbon reduction, collaborative governance and ecological cycle, carbon dioxide capture/transportation/Storage and non-carbon dioxide greenhouse gas emission reduction and other key technologies for terminal emission reduction.
carbon zero emission key technology (zero carbon): Develop new solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, ocean energy, biomass energy, nuclear energy and other zero-carbon power technologies, as well as mechanical energy, thermochemistry, electrochemical and other energy storage technologies, Strengthen the research on advanced energy Internet technologies such as high-proportion renewable energy grid connection, UHV transmission, new DC power distribution, and distributed energy. Develop zero-carbon non-electric energy technologies such as renewable energy/resource hydrogen production, hydrogen storage, hydrogen transportation and hydrogen use technologies, and low-grade waste heat utilization. Develop zero-carbon raw material/fuel substitution technologies such as biomass utilization, ammonia energy utilization, waste recycling, non-fluorine-containing gas utilization, and energy recycling. Develop zero-carbon industrial process reengineering technology in key industries such as iron and steel, chemical industry, building materials, petrochemical and nonferrous metals.
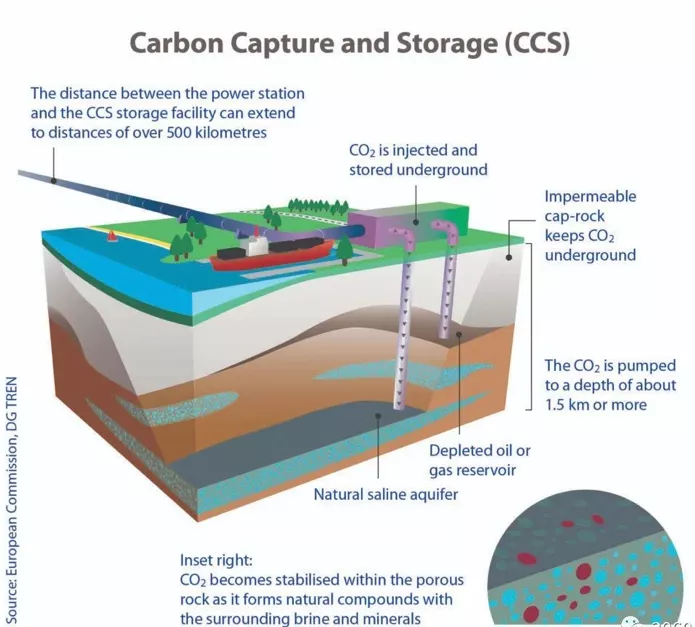
key carbon negative emission technologies (negative carbon): strengthen the geological utilization of carbon dioxide, the efficient conversion of carbon dioxide into fuel chemicals, direct air carbon dioxide capture, biochar soil improvement and other carbon negative emission technology innovations; research on carbon negative emission technologies and mitigation and adaptation The synergistic relationship between climate change leads the construction of an ecologically safe negative emission technology system; tackling the core difficulties of carbon sequestration technology, strengthen the upgrading of carbon sequestration technologies for forests, grasslands, wetlands, oceans, soils, and frozen soils, and enhance the carbon sequestration of ecosystems.

As far as China's national conditions are concerned, power, steel, construction and other industries have become key areas with high energy consumption and high emissions. How can these industries develop low-carbon technologies?
the three major areas of high energy consumption and high emission industries.
the
first is the power industry. at present, China emits 0.8-0.9kg of carbon dioxide per kilowatt-hour of electricity. If the coal consumption per kilowatt-hour is reduced by 1 gram, the country can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 7.5 million tons per year. Therefore, efforts should be concentrated on accelerating technological transformation, promoting thermal power emission reduction, and implementing the "green coal power" plan. This will mainly rely on the development of clean coal conversion and efficient utilization technology and the improvement of coal-fired power generation efficiency, in which the improvement of coal-fired power generation efficiency can achieve 15% emission reduction. At present, the promising efficient and clean coal power generation technology mainly involves technologies such as integrated gasification combined cycle (IGC) and circulating fluidized bed combustion (CFBC). The
of
 is the material and manufacturing field, which mainly focuses on two aspects: the
is the material and manufacturing field, which mainly focuses on two aspects: the
of
is metal material manufacturing. In 2010, China's crude steel output will reach 0.66 billion tons, and the energy consumption of the iron and steel industry will account for 1/4 of the country's total industrial energy consumption. For every ton of steel produced, 2 tons of carbon dioxide will be emitted by blast furnace process and 1 ton of carbon dioxide will be emitted by electric furnace process. The iron and steel industry must combine controlling the total amount, eliminating backward and technological transformation to promote energy conservation and emission reduction.
II is polymer materials. In 2009, China produced 40 million tons of plastics. If we take polymer materials prepared by petroleum routes as an example, it is estimated that for every ton of plastic produced, 2-5 tons of crude oil will be consumed and 4-8 tons of carbon dioxide will be emitted. Therefore, on the one hand, we must vigorously develop new stabilization technologies to increase the service life of materials, thereby saving petrochemical resources and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. On the other hand, through the application of bio-based and biodegradable plastic technology, renewable resources can be directly replaced by petrochemical resources, while accelerating the development of efficient recycling new technologies. If an industrial chain is formed from raw materials to recycling, taking an annual output of 10 million tons of bio-based materials as an example, the unit product can reduce carbon dioxide emissions by more than 40%.
of
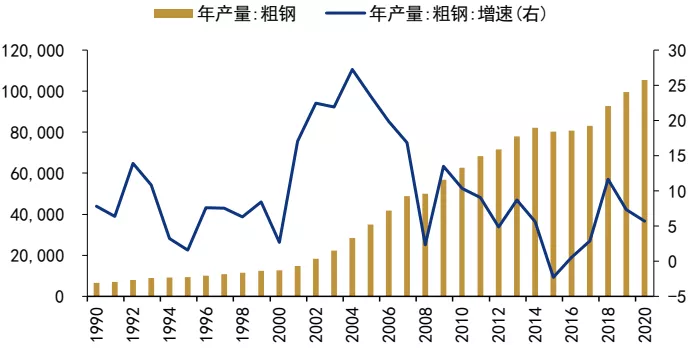 Figure 1: China's Crude Steel Annual Output and Growth Rate (Unit: 10,000 Tons,%)
Figure 1: China's Crude Steel Annual Output and Growth Rate (Unit: 10,000 Tons,%)
Source: Wind Information, Far East Credit Sorting 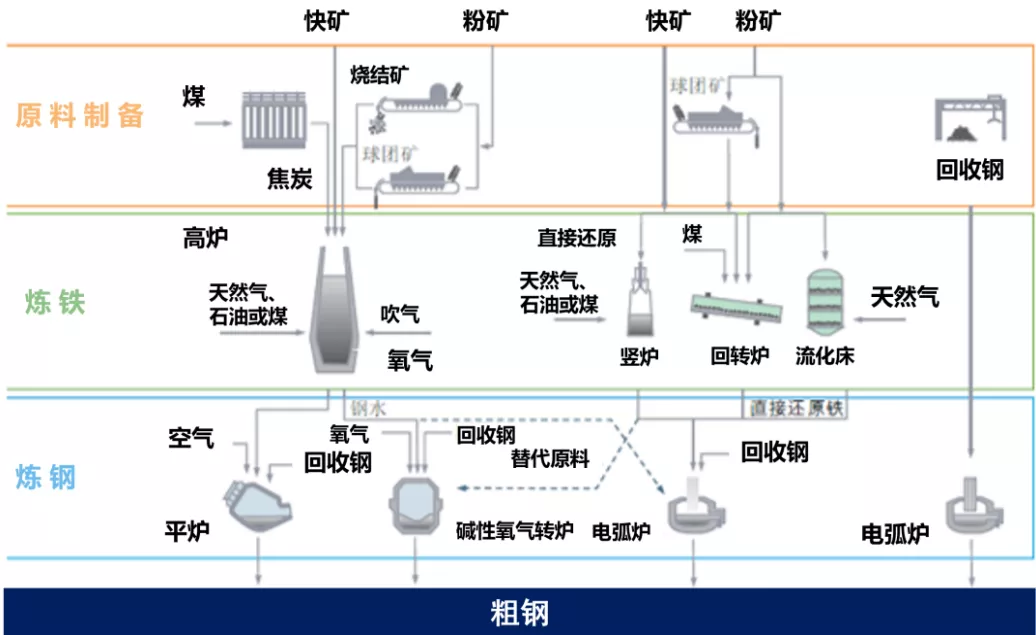
Figure 2: Crude Steel Main Production Process Route
Source: International Iron and Steel Association, Far East Credit Sorting 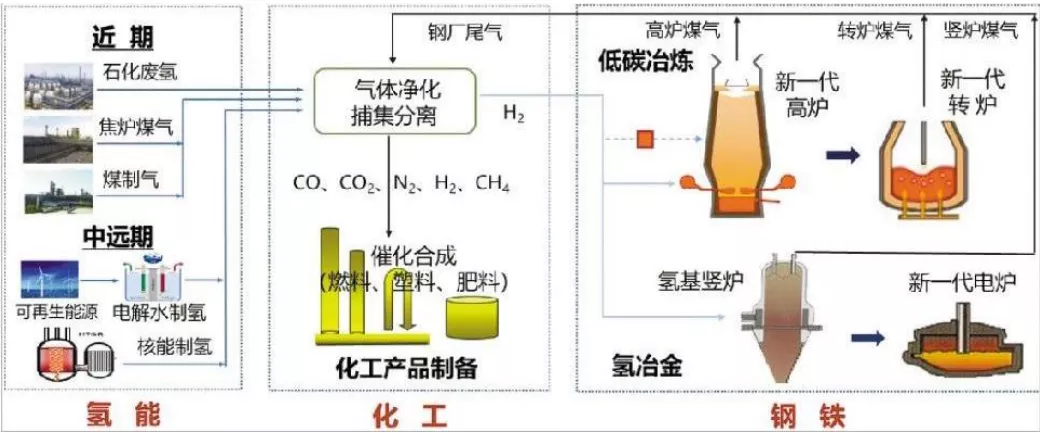 of
of
Figure 3: Steel-Chemical-Hydrogen Energy Integrated Network Integrated Intelligent Manufacturing
Source: northeastern University Iron and Steel Frontier Technology Research Institute, Far East Credit Sorting
The third is the construction field. The current 60% of urban carbon emissions comes from the building maintenance function itself. It is extremely important to build a green building technology system and develop low-carbon buildings. The key is low-carbon control optimization in the whole process of building planning and design, construction, use, operation, maintenance, demolition and reuse. For example, in the construction link, roof photovoltaic power generation technology can be used to realize the effective integration of natural light and lighting. Unpowered roof ventilation equipment can be built to adjust the wind speed and drive the fan to generate electricity; in the use link, the "green roof" can be built by planting roof flowers and plants, which can not only achieve the cooling effect, save air-conditioning power, but also absorb air pollutants; in the demolition link, construction waste can be effectively recycled, prevent secondary pollution.
released "China Building Energy Consumption Research Report (2020)" according to China Building Energy Conservation Association. The "Research Report" introduces the measurement method of energy consumption and carbon emissions in the whole building process, data analysis, and the carbon emission scenarios of buildings under the carbon neutralization target.
"Research Report" shows that during the period 2005-2018, the proportion of energy consumption in the whole building process showed an upward trend, and the proportion of carbon emissions showed a downward trend. In 2000-2018, the national energy consumption center of gravity shifted 0.9 degrees (latitude) to the south, and the carbon emission center of gravity shifted 1.1 degrees (latitude) to the south, with a more obvious movement trend. Measurement of energy consumption and carbon emissions in the whole process of
buildings:
sources: Peking University Financial Review, Pan Energy Big Data Knowledge Service, China Building Energy Conservation Association Energy Consumption Statistics Committee
* Disclaimer: The content contained in it comes from public channels such as the Internet and WeChat public number, and we maintain a neutral attitude towards the views in this article. This article is for reference only. The copyright of the reprinted manuscript belongs to the original author and organization. If there is infringement, please contact Huayi Tianxia customer service to delete
it.
 Mainly
Mainly

 Polyurethane
Polyurethane

 Fine Chemical
Fine Chemical





 Divide the above picture into two parts for easy reading (please watch it horizontally)
Divide the above picture into two parts for easy reading (please watch it horizontally) 




 is the material and manufacturing field, which mainly focuses on two aspects: the
is the material and manufacturing field, which mainly focuses on two aspects: the  Figure 1: China's Crude Steel Annual Output and Growth Rate (Unit: 10,000 Tons,%)
Figure 1: China's Crude Steel Annual Output and Growth Rate (Unit: 10,000 Tons,%) 
 of
of 









.png)



